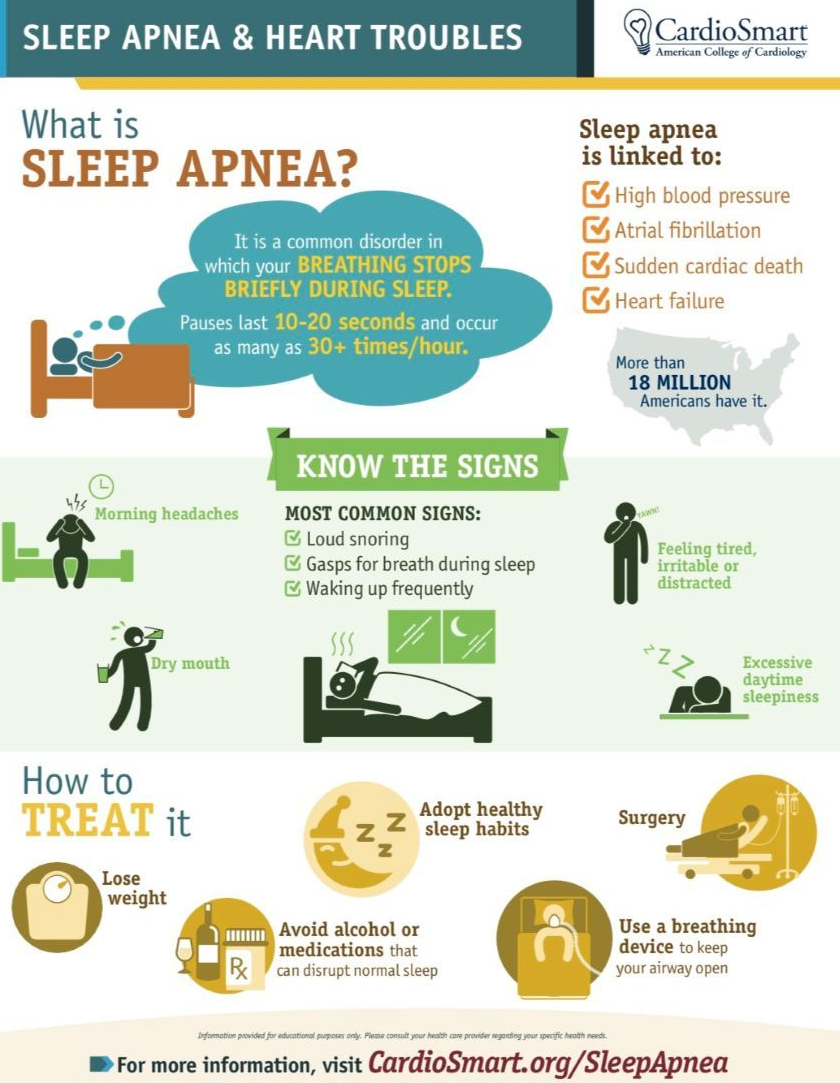
Health Infographics: “What Is Sleep Apnea”



Hospitals across the U.S. are experiencing an influx of COVID-19 patients, but clinicians are reportedly seeing fewer patients going to the emergency room for heart attack or stroke.
Experts worry that patients who need critical care are delaying their treatment over COVID-19 concerns.
To encourage patients to pay close attention to their symptoms and call 9-1-1 immediately if they believe they are having a heart attack or stroke, ACC’s CardioSmart team developed the Coronavirus and Your Heart Infographic.
The infographic urges patients not to ignore symptoms, especially if they have a heart condition, and reassures them that hospitals have safety measures to protect patients from infection with the novel coronavirus.
From a MedPageToday.com online article (March 2, 2020):
 “Dysfunctional sleep likely is by far the most prevalent comorbidity in CVD. This makes it essential to explore the nature of sleep, but this is reliant on the enthusiasm of clinician scientists,” according to the editorialists.
“Dysfunctional sleep likely is by far the most prevalent comorbidity in CVD. This makes it essential to explore the nature of sleep, but this is reliant on the enthusiasm of clinician scientists,” according to the editorialists.
“In modern society, both the quantity and quality of sleep are negatively influenced by factors such as longer hours of work, more shift work, artificial light and cell phones, all leading to self-reported daytime symptoms such as fatigue, tiredness, and sleepiness,”
A larger range in individual sleep duration and sleep timing across 7 days of wrist actigraphy was associated with significantly more CVD events over a median 4.9 years of follow-up (P=0.002 for both trends).
From a European Society of Cardiology online release:
 The annual rate of death from cardiovascular disease was nearly four times higher in women with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (2.2% versus 0.6%). Annual cancer deaths were doubled in patients with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (0.9% versus 0.4%). The annual rate of death from other causes was more than four times higher in those with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (1.4% vs. 0.3%).
The annual rate of death from cardiovascular disease was nearly four times higher in women with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (2.2% versus 0.6%). Annual cancer deaths were doubled in patients with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (0.9% versus 0.4%). The annual rate of death from other causes was more than four times higher in those with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (1.4% vs. 0.3%).
Women who can exercise vigorously are at significantly lower risk of dying from heart disease, cancer and other causes. The research is presented today at EuroEcho 2019, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
During a median follow-up of 4.6 years there were 345 cardiovascular deaths, 164 cancer deaths, and 203 deaths from other causes. After adjusting for factors that could influence the relationship, METs were significantly associated with lower risk of death from cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other causes.
To read more: https://www.escardio.org/The-ESC/Press-Office/Press-releases/Women-exercise-and-longevity