
Where Perseverance Meets Discovery
On the power of cathedral-building in science.
The Ice at the Far Ends of Earth
Researchers know the planet’s ice is melting; now, they are uncovering what that will mean for all of us.

On the power of cathedral-building in science.
Researchers know the planet’s ice is melting; now, they are uncovering what that will mean for all of us.
Caltech Magazine (November 8, 2024): The FAll 2024 issue features ‘Chemical Codebreakers’ – Isotopes help scientists open window to the past….
Journeys to the Past: Isotope geochemistry is helping scientists reveal secrets about the molecular histories of Earth, the cosmos, the human body, and more.
An Intriguing Red Planet Rock: The Mars Perseverance rover has found a “compelling” rock that could indicate the planet hosted microbial life billions of years ago.
The 2024 Distinguished Alumni: Meet this year’s awardees: David Brin (BS ’73), Louise Chow (PhD ’73), Bill Coughran (BS, MS ’75), and Timothy M. Swager (PhD ’88).
The Evolution of Trolling: A new theoretical framework explains why social media discourse can be so toxic.
Inside Look: Joe Parker: Step into the office of this evolutionary biologist, whose research nest is filled with real—and illustrated— insects.
Ripples from the Heart: Mory Gharib (PhD ’83) has leveraged his aerospace expertise to tease out some of the heart’s greatest secrets and use them to develop life-saving medical devices.
The Lab in the Sky Says Goodbye: A NASA DC-8 airplane that carried Caltech students around the globe for science has been retired.

In January, researchers developed a cage-like vaccine platform called a mosaic nanoparticle that could help protect against multiple strains of coronavirus; obtained new insights into human decision-making using AI-trained networks playing video games; learned how tiny plants changed the planet nearly half a billion years ago; and studied chaotic systems using a camera that can take up to 70 trillion frames per second.
Meanwhile, the Institute announced that it would remove the names of known eugenics proponents from its buildings, honors, and assets.
February saw the historic landing of NASA’s Mars rover Perseverance on the Red Planet. The 2,263-pound rover, designed and operated by JPL, which Caltech manages for NASA, will spend two years investigating Mars’s Jezero crater, and will collect and cache samples of rocks and sediment for recovery by a subsequent mission.
Here on Earth, seismologists worked with optics experts to develop a method to use existing underwater telecommunication cables to detect earthquakes; physicists advanced the use of exotic materials for future ultrafast computers; and engineers perfected methods to place molecules in particular orientations at specific locations—work that paves the way for the integration of molecules with computer chips.
In March, Caltech researchers announced a non-invasive method that uses ultrasound to read and interpret brain activity related to the intent to move, a major step toward the creation of noninvasive brain–machine implants that can restore movement to paralyzed individuals; located Mars’s missing water; described a long-sought solution to “one of the most stubborn problems in math”; and explained how bacteria evolve resistance to antibiotics and how antibiotics help bacteria eat when nutrients are scarce.
Gao has developed a new way to power wireless wearable sensors: He harvests kinetic energy that is produced by a person as they move around.

“Our triboelectric generator, also called a nanogenerator, has a stator, which is fixed to the torso, and a slider, which is attached to the inside of the arm. The slider slides against the stator during human motion, and, an electrical current is generated at the same time,” Gao says. “The mechanism is quite simple. Friction results in electrical generation. This is not something new, concept-wise.”

This energy harvesting is done with a thin sandwich of materials (Teflon, copper, and polyimide) that are attached to the person’s skin. As the person moves, these sheets of material rub against a sliding layer made of copper and polyimide, and generate small amounts of electricity. The effect, known as triboelectricity, is perhaps best illustrated by the static electric shock a person might receive after walking across a carpeted floor and then touching a metal doorknob.
From a CalTech news article (February 4, 2020):
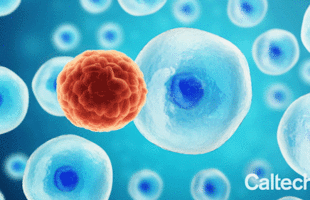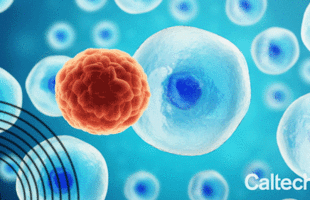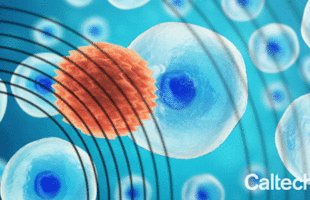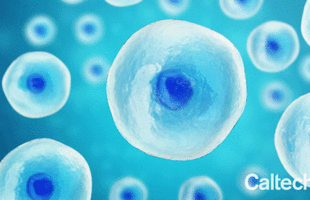 The hope, Lee says, is that ultrasound will kill cancer cells in a specific way that will also engage the immune system and arouse it to attack any cancer cells remaining after the treatment.
The hope, Lee says, is that ultrasound will kill cancer cells in a specific way that will also engage the immune system and arouse it to attack any cancer cells remaining after the treatment.
A new technique could offer a targeted approach to fighting cancer: low-intensity pulses of ultrasound have been shown to selectively kill cancer cells while leaving normal cells unharmed.
 Ultrasound waves—sound waves with frequencies higher than humans can hear—have been used as a cancer treatment before, albeit in a broad-brush approach: high-intensity bursts of ultrasound can heat up tissue, killing cancer and normal cells in a target area. Now, scientists and engineers are exploring the use of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in an effort to create a more selective treatment.
Ultrasound waves—sound waves with frequencies higher than humans can hear—have been used as a cancer treatment before, albeit in a broad-brush approach: high-intensity bursts of ultrasound can heat up tissue, killing cancer and normal cells in a target area. Now, scientists and engineers are exploring the use of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in an effort to create a more selective treatment.
A study describing the effectiveness of the new approach in cell models was published in Applied Physics Letters on January 7. The researchers behind the work caution that it is still preliminary—it still has not been tested in a live animal let alone in a human, and there remain several key challenges to address—but the results so far are promising.
From a CalTech Matters online article:

“Observation is observation. Looking, listening, thinking, conjecturing … all original ideas begin with a kind of scrutiny that is at once framed by discipline and open to discovery. Because I have always taught students in a university, not in an art school, I think I have a baseline understanding of what it means to approach the visual world from a different place. Teaching non-artists is always a little bit like being a foreign exchange student. Therein lies the challenge—and, I suspect, the fun.”
January 7, 2020 – This month, artist, designer, and writer Jessica Helfand joins Caltech as the Winter 2020 artist-in-residence in the Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences’ Caltech-Huntington Program in Visual Culture, which is administered jointly by the division and The Huntington Library, Art Museum, and Botanical Gardens. Helfand is a former contributing editor and columnist for Print, Eye and Communications Arts magazines, and founding editor of the website Design Observer. She taught at Yale for two decades and has held artist residencies at the American Academy in Rome and the Bogliasco Foundation, among others. Her most recent book, Face: A Visual Odyssey, was published by MIT Press last fall. On January 16, Helfand will take part in a noontime talk with Bren Professor of Psychology, Neuroscience, and Biology Ralph Adolphs on the theme of the “face.”

From a Caltech online article:
 During this decade, as in previous decades, Caltech scientists and engineers reinvented the landscape of scientific endeavor: from the first detection of gravitational waves and the discovery of evidence for a ninth planet in the solar system; to bold missions to explore and understand the solar system; to the development of new methods to see inside the body and the brain and understand the universe around us; to the invention of devices to improve human health, some taking inspiration from nature; to the initiation of a transformative new effort to support research into the most pressing challenges in environmental sustainability.
During this decade, as in previous decades, Caltech scientists and engineers reinvented the landscape of scientific endeavor: from the first detection of gravitational waves and the discovery of evidence for a ninth planet in the solar system; to bold missions to explore and understand the solar system; to the development of new methods to see inside the body and the brain and understand the universe around us; to the invention of devices to improve human health, some taking inspiration from nature; to the initiation of a transformative new effort to support research into the most pressing challenges in environmental sustainability.
 Though the brain orchestrates how we experience the world, many questions remain about its complex workings. During the past 10 years, Caltech scientists have discovered how the brain recognizes faces and drives and quenches thirst, and learned about the pathways that govern sleep. A major focus has been on understanding the experience of non-neurotypical individuals, such as those who have autism or those who are missing a brain hemisphere. New realms of neuroscience research were made possible in 2016, when philanthropists Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen announced a gift to establish the Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute for Neuroscience at Caltech.
Though the brain orchestrates how we experience the world, many questions remain about its complex workings. During the past 10 years, Caltech scientists have discovered how the brain recognizes faces and drives and quenches thirst, and learned about the pathways that govern sleep. A major focus has been on understanding the experience of non-neurotypical individuals, such as those who have autism or those who are missing a brain hemisphere. New realms of neuroscience research were made possible in 2016, when philanthropists Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen announced a gift to establish the Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute for Neuroscience at Caltech.
 As modern technology advances, so do the possibilities for treating medical conditions that were previously considered untreatable. Caltech researchers used an electrode array to help a paralyzed patient stand and move his legs voluntarily and developed a novel method for preventing the spread of diseases, contact lenses for preventing blindness in diabetic patients, an app that monitors heart health, gene therapy for repairing nerves in the brain, and a robotic arm controlled by a paralyzed patient’s intent to move. The decade also saw the establishment of the Merkin Institute for Translational Research, which aims to advance medical technologies, and a continued commitment to the Donna and Benjamin M. Rosen Bioengineering Center.
As modern technology advances, so do the possibilities for treating medical conditions that were previously considered untreatable. Caltech researchers used an electrode array to help a paralyzed patient stand and move his legs voluntarily and developed a novel method for preventing the spread of diseases, contact lenses for preventing blindness in diabetic patients, an app that monitors heart health, gene therapy for repairing nerves in the brain, and a robotic arm controlled by a paralyzed patient’s intent to move. The decade also saw the establishment of the Merkin Institute for Translational Research, which aims to advance medical technologies, and a continued commitment to the Donna and Benjamin M. Rosen Bioengineering Center.
To read more: https://www.caltech.edu/about/news/decade-of-discovery
From a Caltech online news release:
 “Such wearable sweat sensors have the potential to rapidly, continuously, and noninvasively capture changes in health at molecular levels,” Gao says. “They could enable personalized monitoring, early diagnosis, and timely intervention.”
“Such wearable sweat sensors have the potential to rapidly, continuously, and noninvasively capture changes in health at molecular levels,” Gao says. “They could enable personalized monitoring, early diagnosis, and timely intervention.”
The development of such sensors would allow doctors to continuously monitor the condition of patients with illnesses like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or kidney disease, all of which result in abnormal levels of nutrients or metabolites in the bloodstream. Patients would benefit from having their physician better informed of their condition, while also avoiding invasive and painful encounters with hypodermic needles.
 Gao’s work is focused on developing devices based on microfluidics, a name for technologies that manipulate tiny amounts of liquids, usually through channels less than a quarter of a millimeter in width. Microfluidics are ideal for an application of this sort because they minimize the influence of sweat evaporation and skin contamination on the sensing accuracy. As freshly supplied sweat flows through the microchannels, the device can make more accurate measurements of sweat and can capture temporal changes in concentrations.
Gao’s work is focused on developing devices based on microfluidics, a name for technologies that manipulate tiny amounts of liquids, usually through channels less than a quarter of a millimeter in width. Microfluidics are ideal for an application of this sort because they minimize the influence of sweat evaporation and skin contamination on the sensing accuracy. As freshly supplied sweat flows through the microchannels, the device can make more accurate measurements of sweat and can capture temporal changes in concentrations.
To read more: https://www.caltech.edu/about/news/wearable-sweat-sensor-detects-gout-causing-compounds
From a Caltech online article:
 When a bee lands on water, the water sticks to its wings, robbing it of the ability to fly. However, that stickiness allows the bee to drag water, creating waves that propel it forward. In the lab, Roh and Gharib noted that the generated wave pattern is symmetrical from left to right. A strong, large-amplitude wave with an interference pattern is generated in the water at the rear of the bee, while the surface in front of the bee lacks the large wave and interference. This asymmetry propels the bees forward with the slightest of force—about 20 millionths of a Newton.
When a bee lands on water, the water sticks to its wings, robbing it of the ability to fly. However, that stickiness allows the bee to drag water, creating waves that propel it forward. In the lab, Roh and Gharib noted that the generated wave pattern is symmetrical from left to right. A strong, large-amplitude wave with an interference pattern is generated in the water at the rear of the bee, while the surface in front of the bee lacks the large wave and interference. This asymmetry propels the bees forward with the slightest of force—about 20 millionths of a Newton.
Walking on Caltech’s campus, research engineer Chris Roh (MS ’13, PhD ’17) happened to see a bee stuck in the water of Millikan Pond. Although it was a common-enough sight, it led Roh and his advisor, Mory Gharib (PhD ’83), to a discovery about the potentially unique way that bees navigate the interface between water and air.
To read more: https://www.caltech.edu/about/news/bees-surf-atop-water