From a The Lancet online article:
 As a consultant, I had profoundly failed to appreciate the experience of fatigue and apathy among patients. More than excessive tiredness, the fatigue was overwhelming, turning simple activities into insurmountable, exhausting challenges. It was frustrating and I fell into the trap of overexertion when I did have energy, thus exhausting myself and sabotaging the day’s recovery plan. Had staff not been so adept at encouraging me when I lacked energy and holding me back when I tried to overdo things, I would have squandered much valuable rehabilitation time.
As a consultant, I had profoundly failed to appreciate the experience of fatigue and apathy among patients. More than excessive tiredness, the fatigue was overwhelming, turning simple activities into insurmountable, exhausting challenges. It was frustrating and I fell into the trap of overexertion when I did have energy, thus exhausting myself and sabotaging the day’s recovery plan. Had staff not been so adept at encouraging me when I lacked energy and holding me back when I tried to overdo things, I would have squandered much valuable rehabilitation time.
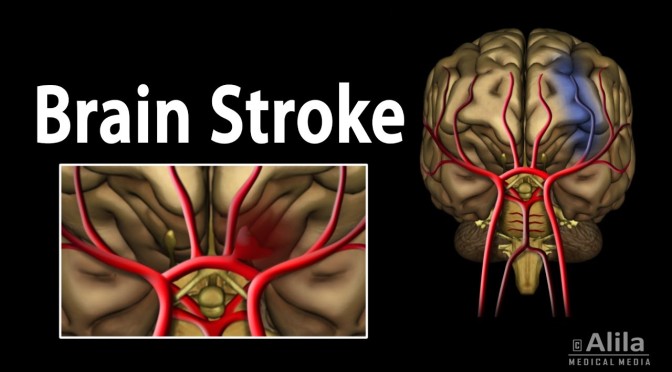
I was a consultant in neurological rehabilitation for acquired brain injury when, at the age of 62 years, I had a stroke. Running for a train, I experienced pain in the right side of my head and mild weakness and sensory loss in my left limbs. I thought I’d had a stroke, but I was remarkably calm. It was late and my instinct was to get home, where I went to the study. In the morning, I found myself on the floor, half-blind, half-paralysed, and terrified.
.
Scans showed a large intracerebral haemorrhage in the area of the right basal ganglia. My symptoms could be explained by the damage to my brain—my medical world was in order, something to hold on to. I discussed my diagnosis and treatment with my colleagues during brief waking periods, grateful that they still saw the person I was before my stroke. Meanwhile, my wife was in the good hands of staff who treated her with sensitivity, giving her plain facts and support.
 As a consultant, I had profoundly failed to appreciate the experience of fatigue and apathy among patients. More than excessive tiredness, the fatigue was overwhelming, turning simple activities into insurmountable, exhausting challenges. It was frustrating and I fell into the trap of overexertion when I did have energy, thus exhausting myself and sabotaging the day’s recovery plan. Had staff not been so adept at encouraging me when I lacked energy and holding me back when I tried to overdo things, I would have squandered much valuable rehabilitation time.
As a consultant, I had profoundly failed to appreciate the experience of fatigue and apathy among patients. More than excessive tiredness, the fatigue was overwhelming, turning simple activities into insurmountable, exhausting challenges. It was frustrating and I fell into the trap of overexertion when I did have energy, thus exhausting myself and sabotaging the day’s recovery plan. Had staff not been so adept at encouraging me when I lacked energy and holding me back when I tried to overdo things, I would have squandered much valuable rehabilitation time. 
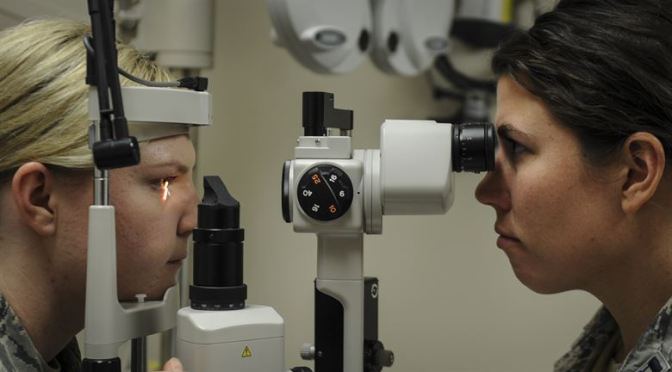
 Our 3D deep-learning system performed well in both primary and external validations, suggesting that it could potentially be used for automated detection of glaucomatous optic neuropathy based on SDOCT volumes. Screening with the deep-learning system is much faster than conventional glaucoma screening methods (ie, by experienced specialists), can be done automatically, and does not require a large number of trained personnel on site. Further prospective studies are warranted to estimate the incremental cost-effectiveness of incorporating this artificial intelligence-based model for screening for glaucoma, both in the general population and among at-risk people.
Our 3D deep-learning system performed well in both primary and external validations, suggesting that it could potentially be used for automated detection of glaucomatous optic neuropathy based on SDOCT volumes. Screening with the deep-learning system is much faster than conventional glaucoma screening methods (ie, by experienced specialists), can be done automatically, and does not require a large number of trained personnel on site. Further prospective studies are warranted to estimate the incremental cost-effectiveness of incorporating this artificial intelligence-based model for screening for glaucoma, both in the general population and among at-risk people.
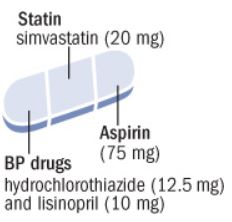 Use of polypill was effective in preventing major cardiovascular events. Medication adherence was high and adverse event numbers were low. The polypill strategy could be considered as an additional effective component in controlling cardiovascular diseases, especially in LMICs.
Use of polypill was effective in preventing major cardiovascular events. Medication adherence was high and adverse event numbers were low. The polypill strategy could be considered as an additional effective component in controlling cardiovascular diseases, especially in LMICs.
 2 years of moderate calorie restriction significantly reduced multiple cardiometabolic risk factors in young, non-obese adults. These findings suggest the potential for a substantial advantage for cardiovascular health of practicing moderate calorie restriction in young and middle-aged healthy individuals, and they offer promise for pronounced long-term population health benefits.
2 years of moderate calorie restriction significantly reduced multiple cardiometabolic risk factors in young, non-obese adults. These findings suggest the potential for a substantial advantage for cardiovascular health of practicing moderate calorie restriction in young and middle-aged healthy individuals, and they offer promise for pronounced long-term population health benefits.
 This joint position statement from the International Atherosclerosis Society and the International Chair on Cardiometabolic Risk Working Group on Visceral Obesity summarises the evidence for visceral adiposity and ectopic fat as emerging risk factors for type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease, with a focus on practical recommendations for health professionals and future directions for research and clinical practice.
This joint position statement from the International Atherosclerosis Society and the International Chair on Cardiometabolic Risk Working Group on Visceral Obesity summarises the evidence for visceral adiposity and ectopic fat as emerging risk factors for type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease, with a focus on practical recommendations for health professionals and future directions for research and clinical practice.


 “Knee replacement is increasing in frequency, and it has an associated substantial cost implication to any health-care provider. It is also essential that patients receive the most efficacious operation for this condition. Before our study, and despite several cohort-based reports, knowledge of whether one operation type is superior, remained uncertain. Our 5-year study has indicated that both TKR and PKR are beneficial interventions but, based on our combined clinical and cost-effectiveness data and providing the operation is performed by those with adequate experience, we recommend that PKR should be offered as the treatment of choice for late-stage isolated medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee.
“Knee replacement is increasing in frequency, and it has an associated substantial cost implication to any health-care provider. It is also essential that patients receive the most efficacious operation for this condition. Before our study, and despite several cohort-based reports, knowledge of whether one operation type is superior, remained uncertain. Our 5-year study has indicated that both TKR and PKR are beneficial interventions but, based on our combined clinical and cost-effectiveness data and providing the operation is performed by those with adequate experience, we recommend that PKR should be offered as the treatment of choice for late-stage isolated medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee.

 From time immemorial, an invariable feature of doctor–patient interaction has been that it takes place in person. But the status quo is changing. A large portion of patient care might eventually be delivered via telemedicine by virtualists, physicians who treat patients they may never meet.
From time immemorial, an invariable feature of doctor–patient interaction has been that it takes place in person. But the status quo is changing. A large portion of patient care might eventually be delivered via telemedicine by virtualists, physicians who treat patients they may never meet.