From a Scientic American online article:
 In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.
In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.
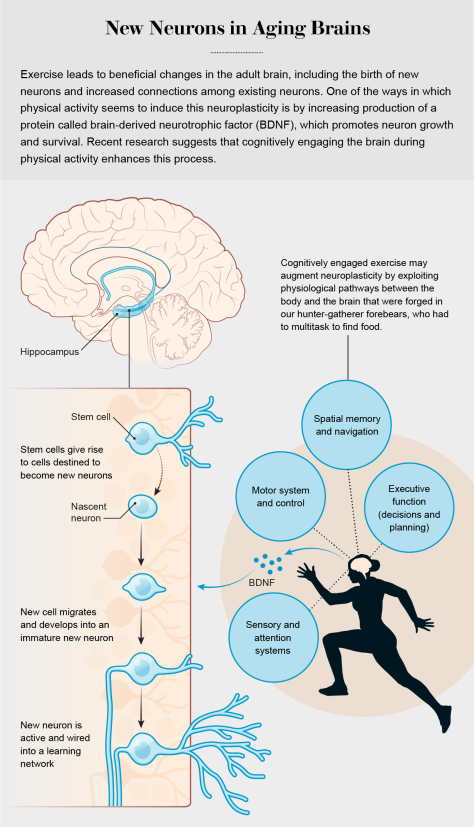
In fact, a growing body of research suggests that exercise that is cognitively stimulating may indeed benefit the brain more than exercise that does not make such cognitive demands. For example, Gerd Kempermann and his colleagues at the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden in Germany explored this possibility by comparing the growth and survival of new neurons in the mouse hippocampus after exercise alone or after exercise combined with access to a cognitively enriched environment. They found an additive effect: exercise alone was good for the hippocampus, but combining physical activity with cognitive demands in a stimulating environment was even better, leading to even more new neurons. Using the brain during and after exercise seemed to trigger enhanced neuron survival.
To read more: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/why-your-brain-needs-exercise/





 tes of Health’s largest loan repayment program was conceived to help scientists pay off school debts without relying on industry funding. But
tes of Health’s largest loan repayment program was conceived to help scientists pay off school debts without relying on industry funding. But 
 Byer also helped develop the quietest, most stable laser in the world, called the diode-pumped YAG laser. YAG lasers are today found in everything from communications satellites to green handheld laser pointers, which Byer co-developed with two of his graduate students and cites as one of his favorite inventions (he had joined Stanford in 1969). YAG lasers also form the main beams of the gravitational wave-detecting instrument, LIGO, which in 2015 achieved the most precise measurement ever made by humans when its antenna detected the tenuous spacetime fluctuations generated by two colliding black holes 1.3 billion light-years away.
Byer also helped develop the quietest, most stable laser in the world, called the diode-pumped YAG laser. YAG lasers are today found in everything from communications satellites to green handheld laser pointers, which Byer co-developed with two of his graduate students and cites as one of his favorite inventions (he had joined Stanford in 1969). YAG lasers also form the main beams of the gravitational wave-detecting instrument, LIGO, which in 2015 achieved the most precise measurement ever made by humans when its antenna detected the tenuous spacetime fluctuations generated by two colliding black holes 1.3 billion light-years away. One summer morning in 1964, Byer drove the hour from Berkeley down to Mountain View for a job interview at a California company called Spectra Physics. He walked in to find an empty lobby but could hear clapping and cheering in the back of the building. After politely waiting for several minutes, he followed the commotion to a darkened room filled with men whose jubilant faces were illuminated by a rod of red-orange light that seemed to float above an instrument-strewn table
One summer morning in 1964, Byer drove the hour from Berkeley down to Mountain View for a job interview at a California company called Spectra Physics. He walked in to find an empty lobby but could hear clapping and cheering in the back of the building. After politely waiting for several minutes, he followed the commotion to a darkened room filled with men whose jubilant faces were illuminated by a rod of red-orange light that seemed to float above an instrument-strewn table