This presentation by Julia Browne, PhD, a clinical and research fellow in the Center of Excellence for Psychosocial and Systemic Research at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School was part of Schizophrenia Education Day 2019.
This presentation by Julia Browne, PhD, a clinical and research fellow in the Center of Excellence for Psychosocial and Systemic Research at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School was part of Schizophrenia Education Day 2019.
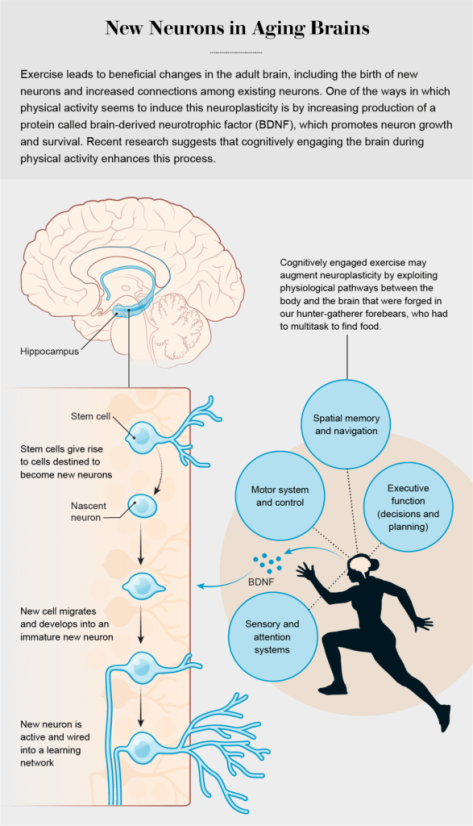

Researchers have also documented clear links between aerobic exercise and benefits to other parts of the brain, including expansion of the prefrontal cortex, which sits just behind the forehead. Such augmentation of this region has been tied to sharper executive cognitive functions, which involve aspects of planning, decision-making and multitasking—abilities that, like memory, tend to decline with healthy aging and are further degraded in the presence of Alzheimer’s. Scientists suspect that increased connections between existing neurons, rather than the birth of new neurons, are responsible for the beneficial effects of exercise on the prefrontal cortex and other brain regions outside the hippocampus.
This interview originally aired Jan. 4, 2020.
From a MD Magazine online release:
 The investigators discovered that patients with a higher genetic risk for depression were more likely to be diagnosed with depression over the next 2 years. However, more physically active patients at baseline were less likely to depression, even after they accounted for genetic risks.
The investigators discovered that patients with a higher genetic risk for depression were more likely to be diagnosed with depression over the next 2 years. However, more physically active patients at baseline were less likely to depression, even after they accounted for genetic risks.
Increasing physical activity could pay dividends for people with a high risk of developing depression.
A team from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) recently discovered that several hours of weekly exercise result in a decreased chance to be diagnosed with a new episode of depression, even in patients with a higher genetic risk of developing Major Depressive Disorder (MDD).
The team examined the genomic and electronic health record (EHR) data of approximately 8000 patients in the Partners Healthcare Biobank, which represents the first study to show how physical activity influences depression despite genetic risk.
From a Science Daily online release:
“People with heart failure cannot do everything that a healthy individual can, so the question becomes how much exercise can they handle and what type of impact will it have on their health,” Emter said. “We found that regardless of intensity level, some type of physical activity was good for heart health compared to no exercise at all.”
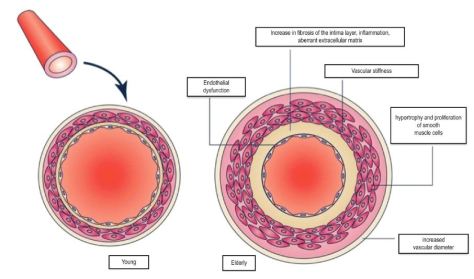
Now, research from the University of Missouri has found exercise can improve the health of blood vessels in the heart for people with heart failure. The finding is based on a study looking at swine, which have very similar blood vessels and heart muscles — both structurally and functionally — as humans.
To read more: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/10/191022174402.htm
 “Living a healthy lifestyle may help offset a person’s genetic risk of dementia, according to new research.
“Living a healthy lifestyle may help offset a person’s genetic risk of dementia, according to new research.
The study was led by the University of Exeter – simultaneously published today in JAMA and presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2019 in Los Angeles. The research found that the risk of dementia was 32 per cent lower in people with a high genetic risk if they had followed a healthy lifestyle, compared to those who had an unhealthy lifestyle.
Participants with high genetic risk and an unfavourable lifestyle were almost three times more likely to develop dementia compared to those with a low genetic risk and favourable lifestyle.”
To read more click on link below:
http://www.exeter.ac.uk/dementia/news/articles/healthylifestylemayoffset.html