The advent of commercial genome sequencing has recently, and credibly, been compared to the invention of the microscope, a claim that led me to wonder whether this new, still relatively obscure technology, humming away in well-equipped labs around the world, would prove to be the most important innovation of the 21st century.


And unexpectedly, Covid-19 has proved to be the catalyst. “What the pandemic has done is accelerate the adoption of genomics into infectious disease by several years,” says deSouza, the Illumina chief executive. He also told me he believes that the pandemic has accelerated the adoption of genomics into society more broadly — suggesting that quietly, in the midst of chaos and a global catastrophe, the age of cheap, rapid sequencing has arrived.



 “We were able to show that if you can stop the plasmid from replicating, then most of the bacteria lose the plasmid as the bacteria grow and divide. This means that infections that might otherwise be hard to control, even with the most powerful antibiotics available, are more likely to be treatable with standard antibiotics.”
“We were able to show that if you can stop the plasmid from replicating, then most of the bacteria lose the plasmid as the bacteria grow and divide. This means that infections that might otherwise be hard to control, even with the most powerful antibiotics available, are more likely to be treatable with standard antibiotics.”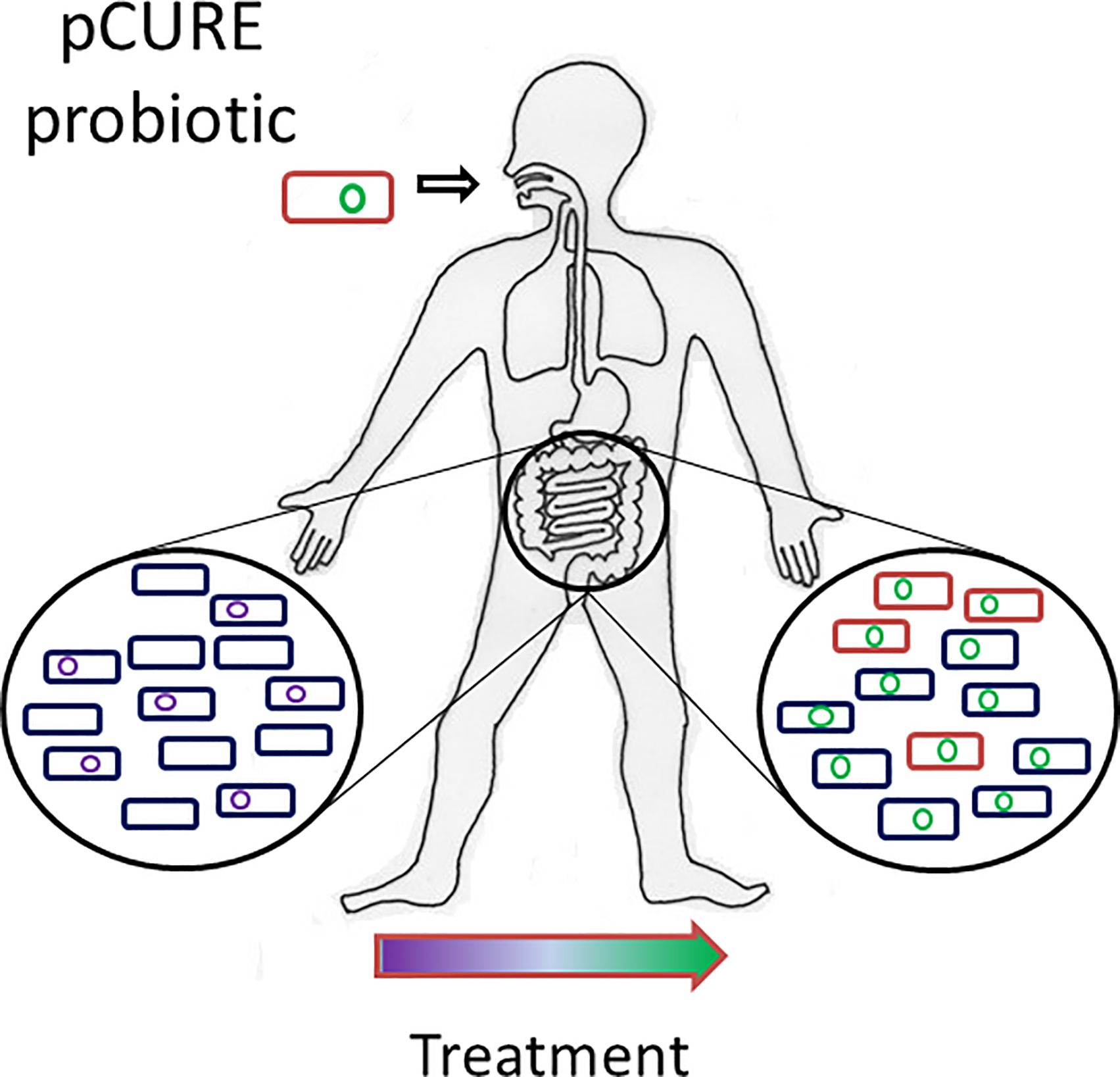

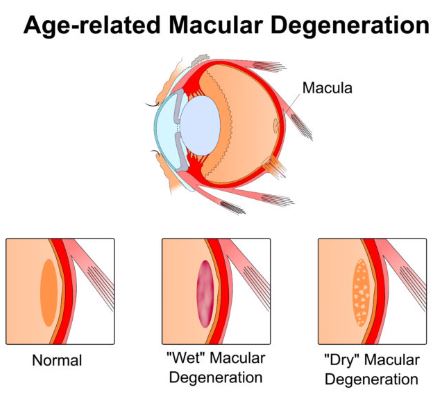 “Our work provides additional evidence that that diet matters,” Millen added. “From a public health standpoint, we can tell people that if you have early AMD, it is likely in your best interest to limit your intake of processed meat, fried food, refined grains, and high-fat dairy to preserve your vision over time.”
“Our work provides additional evidence that that diet matters,” Millen added. “From a public health standpoint, we can tell people that if you have early AMD, it is likely in your best interest to limit your intake of processed meat, fried food, refined grains, and high-fat dairy to preserve your vision over time.”
 “These results show quite clearly that there’s a very specific part of the brain network that’s affected by inflammation,” noted Mazaheri. “This could explain ‘brain fog’.”
“These results show quite clearly that there’s a very specific part of the brain network that’s affected by inflammation,” noted Mazaheri. “This could explain ‘brain fog’.”
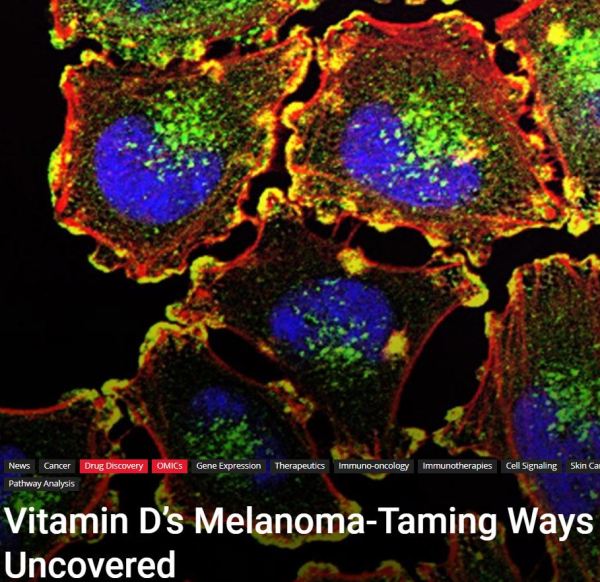 “But what’s really intriguing is that we can now see how vitamin D might help the immune system fight cancer. We know when the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is active in melanoma, it can dampen down the immune response causing fewer immune cells to reach the inside of the tumor, where they could potentially fight the cancer better.
“But what’s really intriguing is that we can now see how vitamin D might help the immune system fight cancer. We know when the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is active in melanoma, it can dampen down the immune response causing fewer immune cells to reach the inside of the tumor, where they could potentially fight the cancer better.