From a New York Times article by Lisa Sanders, M.D.:
 In sarcoidosis, abnormal collections of cells called granulomas invade the organ, interfering with its normal activity and often destroying the surrounding tissue. What is left is a scar, known as fibrosis, dotted with these abnormal granulomas.
In sarcoidosis, abnormal collections of cells called granulomas invade the organ, interfering with its normal activity and often destroying the surrounding tissue. What is left is a scar, known as fibrosis, dotted with these abnormal granulomas.
When caught early, sarcoidosis can be treated and the destruction slowed or even stopped. But it was too late for that in this man’s case. He was started on immune-suppressing medications to prevent additional damage, but he needed a new heart.
The man had been active and healthy, until five years earlier when he started to feel tired. His doctor sent him to a cardiologist, who took one look at his EKG and said he needed a pacemaker, right away. He got one the next day. He was fine for a year, and then, on a business trip to Atlanta, he suddenly felt lightheaded, and his heart fluttered wildly in his chest. In the E.R. they told him his heart was beating 220 beats a minute. You should be dead, one doctor said.
To read more click on the following link: https://www.nytimes.com/2019/08/22/magazine/why-was-the-middle-aged-mans-heart-beating-so-dangerously-fast.html

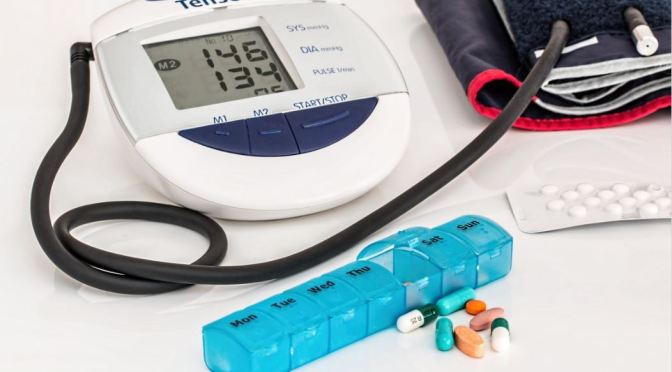

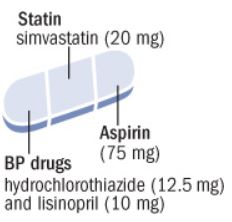 Use of polypill was effective in preventing major cardiovascular events. Medication adherence was high and adverse event numbers were low. The polypill strategy could be considered as an additional effective component in controlling cardiovascular diseases, especially in LMICs.
Use of polypill was effective in preventing major cardiovascular events. Medication adherence was high and adverse event numbers were low. The polypill strategy could be considered as an additional effective component in controlling cardiovascular diseases, especially in LMICs.
 The use of n-3 FA (4 g/d) for improving atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in patients with hypertriglyceridemia is supported by a 25% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events in REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events With EPA Intervention Trial), a randomized placebo-controlled trial of EPA-only in high-risk patients treated with a statin.
The use of n-3 FA (4 g/d) for improving atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in patients with hypertriglyceridemia is supported by a 25% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events in REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events With EPA Intervention Trial), a randomized placebo-controlled trial of EPA-only in high-risk patients treated with a statin.
 Zing’s plan will give seniors access to a network of clinics in Cook County, Illinois, starting in January. The company hopes to expand to three states by 2022. It’s a managed care plan, which means the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) will pay a single monthly fee per member in exchange for a more holistic approach to nurturing patient health. Zing is working with a network of community health centers, including Oak Street Health, which recently raised $65 million for its senior-focused facilities.
Zing’s plan will give seniors access to a network of clinics in Cook County, Illinois, starting in January. The company hopes to expand to three states by 2022. It’s a managed care plan, which means the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) will pay a single monthly fee per member in exchange for a more holistic approach to nurturing patient health. Zing is working with a network of community health centers, including Oak Street Health, which recently raised $65 million for its senior-focused facilities. 
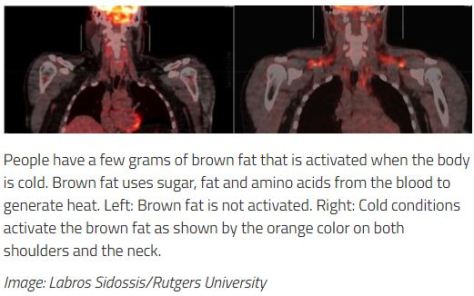

 2 years of moderate calorie restriction significantly reduced multiple cardiometabolic risk factors in young, non-obese adults. These findings suggest the potential for a substantial advantage for cardiovascular health of practicing moderate calorie restriction in young and middle-aged healthy individuals, and they offer promise for pronounced long-term population health benefits.
2 years of moderate calorie restriction significantly reduced multiple cardiometabolic risk factors in young, non-obese adults. These findings suggest the potential for a substantial advantage for cardiovascular health of practicing moderate calorie restriction in young and middle-aged healthy individuals, and they offer promise for pronounced long-term population health benefits.
 This joint position statement from the International Atherosclerosis Society and the International Chair on Cardiometabolic Risk Working Group on Visceral Obesity summarises the evidence for visceral adiposity and ectopic fat as emerging risk factors for type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease, with a focus on practical recommendations for health professionals and future directions for research and clinical practice.
This joint position statement from the International Atherosclerosis Society and the International Chair on Cardiometabolic Risk Working Group on Visceral Obesity summarises the evidence for visceral adiposity and ectopic fat as emerging risk factors for type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease, with a focus on practical recommendations for health professionals and future directions for research and clinical practice.
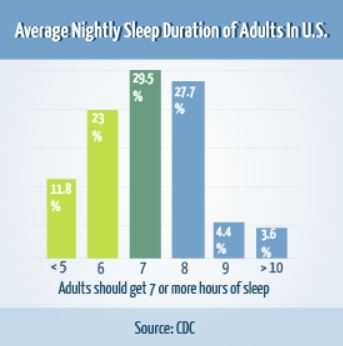 …these results indicate that sleep may play an important role in health disparities and may represent a modifiable risk factor (along with diet and physical activity) for cardiometabolic risk in general and cardiometabolic health disparities specifically.
…these results indicate that sleep may play an important role in health disparities and may represent a modifiable risk factor (along with diet and physical activity) for cardiometabolic risk in general and cardiometabolic health disparities specifically.



