From a PNAS.org online release:
 Our results further suggest that optimism is specifically related to 11 to 15% longer life span, on average, and to greater odds of achieving “exceptional longevity,” that is, living to the age of 85 or beyond. These relations were independent of socioeconomic status, health conditions, depression, social integration, and health behaviors (e.g., smoking, diet, and alcohol use). Overall, findings suggest optimism may be an important psychosocial resource for extending life span in older adults.
Our results further suggest that optimism is specifically related to 11 to 15% longer life span, on average, and to greater odds of achieving “exceptional longevity,” that is, living to the age of 85 or beyond. These relations were independent of socioeconomic status, health conditions, depression, social integration, and health behaviors (e.g., smoking, diet, and alcohol use). Overall, findings suggest optimism may be an important psychosocial resource for extending life span in older adults.
Participants with highest versus lowest optimism levels had 1.5 (women) and 1.7 (men) greater odds of surviving to age 85; these relationships were maintained after adjusting for health behaviors. Given work indicating optimism is modifiable, these findings suggest optimism may provide a valuable target to test for strategies to promote longevity.
To read more: https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2019/08/20/1900712116


 “While we always believed that high levels of uric acid might be bad for kidneys and that patients with gout may have a higher risk of kidney failure, we were quite surprised by the magnitude of the risk imposed by gout in these patients. We were particularly interested in the risk of advanced kidney disease, as these patients in general have a higher risk of kidney failure and death.
“While we always believed that high levels of uric acid might be bad for kidneys and that patients with gout may have a higher risk of kidney failure, we were quite surprised by the magnitude of the risk imposed by gout in these patients. We were particularly interested in the risk of advanced kidney disease, as these patients in general have a higher risk of kidney failure and death.
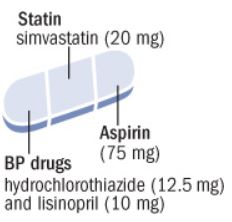 Use of polypill was effective in preventing major cardiovascular events. Medication adherence was high and adverse event numbers were low. The polypill strategy could be considered as an additional effective component in controlling cardiovascular diseases, especially in LMICs.
Use of polypill was effective in preventing major cardiovascular events. Medication adherence was high and adverse event numbers were low. The polypill strategy could be considered as an additional effective component in controlling cardiovascular diseases, especially in LMICs.
 The use of n-3 FA (4 g/d) for improving atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in patients with hypertriglyceridemia is supported by a 25% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events in REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events With EPA Intervention Trial), a randomized placebo-controlled trial of EPA-only in high-risk patients treated with a statin.
The use of n-3 FA (4 g/d) for improving atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in patients with hypertriglyceridemia is supported by a 25% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events in REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events With EPA Intervention Trial), a randomized placebo-controlled trial of EPA-only in high-risk patients treated with a statin.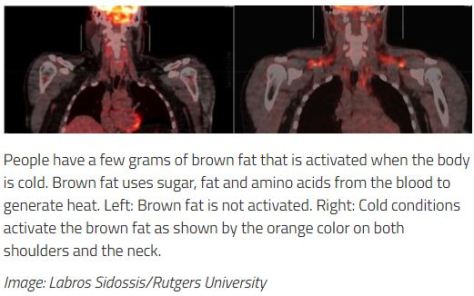

 2 years of moderate calorie restriction significantly reduced multiple cardiometabolic risk factors in young, non-obese adults. These findings suggest the potential for a substantial advantage for cardiovascular health of practicing moderate calorie restriction in young and middle-aged healthy individuals, and they offer promise for pronounced long-term population health benefits.
2 years of moderate calorie restriction significantly reduced multiple cardiometabolic risk factors in young, non-obese adults. These findings suggest the potential for a substantial advantage for cardiovascular health of practicing moderate calorie restriction in young and middle-aged healthy individuals, and they offer promise for pronounced long-term population health benefits.
 This joint position statement from the International Atherosclerosis Society and the International Chair on Cardiometabolic Risk Working Group on Visceral Obesity summarises the evidence for visceral adiposity and ectopic fat as emerging risk factors for type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease, with a focus on practical recommendations for health professionals and future directions for research and clinical practice.
This joint position statement from the International Atherosclerosis Society and the International Chair on Cardiometabolic Risk Working Group on Visceral Obesity summarises the evidence for visceral adiposity and ectopic fat as emerging risk factors for type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease, with a focus on practical recommendations for health professionals and future directions for research and clinical practice.
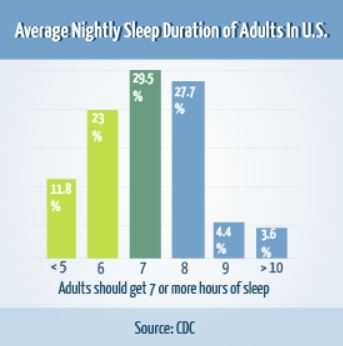 …these results indicate that sleep may play an important role in health disparities and may represent a modifiable risk factor (along with diet and physical activity) for cardiometabolic risk in general and cardiometabolic health disparities specifically.
…these results indicate that sleep may play an important role in health disparities and may represent a modifiable risk factor (along with diet and physical activity) for cardiometabolic risk in general and cardiometabolic health disparities specifically.



