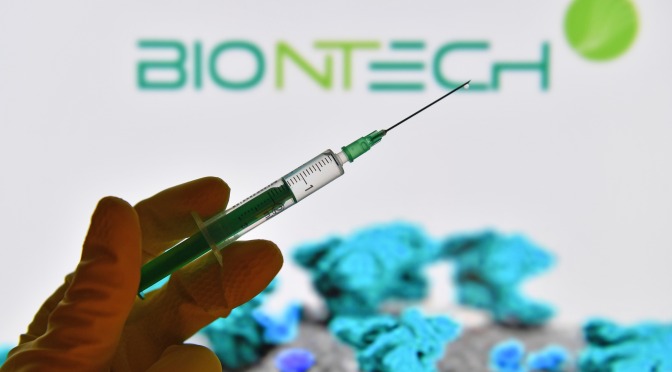
Over a month and a half before the World Health Organization officially declared a pandemic, BioNTech CEO Uğur Şahin met with his wife, BioNTech’s co-founder and chief medical officer Özlem Türeci, and together they agreed to redirect most of the company’s resources to developing a vaccine. Up until that point, BioNTech was little-known internationally and primarily focused on developing novel cancer treatments. The founders were confident in the potential of their mRNA technology, which they knew could trigger a powerful immune response. That confidence wasn’t necessarily shared by the broader medical community. No mRNA vaccine or treatment had ever been approved before. But the couple’s timely breakthrough was actually decades in the making. CNBC spoke with Şahin and Türeci about how they, along with Pfizer, created a Covid-19 vaccine using mRNA.
Tag Archives: Science
Front Covers: Science Magazine – October 22
Front Covers: Nature Magazine – October 21

Science: Vikings In North America, Magnets Moving Non-Magnetic Metals
An ancient solar storm helps pinpoint when Vikings lived in the Americas, and using magnets to deftly move non-magnetic metals.
In this episode:
00:53 Pinpointing Viking presence in North America
It’s well-understood that Vikings went to North America around a thousand years ago. However, working out a precise date has proven difficult. Now, thanks to an ancient solar storm, researchers have been able to identify an individual year when Vikings were definitely living on the continent.
Research article: Kuitems et al.
14:57 Research Highlights
How shoulder muscles gave Pterosaurs an aerodynamic edge, and mysterious radio waves coming from near the centre of the Milky Way.
Research Highlight: How ancient reptiles were streamlined for flight
Research Highlight: A mysterious radio signal object is beaming radio waves into the Milky Way
17:45 Magnets move non-magnetic metals
Scientists have created an array of magnets capable of moving non-metallic objects in 6 dimensions. They hope their new approach could one day be used to clean up debris in space.
Research article: Pham et al.
News and Views: Non-magnetic objects induced to move by electromagnets
27:06 What Francis Collin’s retirement means for the US NIH
After 12 years, Francis Collins announced plans to retire from his role as Director of the United States National Institutes of Health. We discuss his legacy and what this means for the world’s biggest public funder of biomedical research.
Editorial: COVID, racism, China: three tests for the next NIH leader
News: Francis Collins to step down at NIH: scientists assess his legacy
Cover Previews: Scientific American – November 2021
Science: Ripple Effects Of Mass Incarceration, Dog-Sniff Evidence Reliability
This week we are covering the Science special issue on mass incarceration. Can a dog find a body? Sometimes. Can a dog indicate a body was in a spot a few months ago, even though it’s not there now?
There’s not much scientific evidence to back up such claims. But in the United States, people are being sent to prison based on this type of evidence. Host Sarah Crespi talks with Peter Andrey Smith, a reporter and researcher based in Maine, about the science—or lack thereof—behind dog-sniff evidence.
With 2 million people in jail or prison in the United States, it has become incredibly common to have a close relative behind bars. Sarah talks with Hedwig Lee, a sociologist at Washington University in St. Louis, about the consequences of mass incarceration for families of the incarcerated, from economic to social.
Science: Satellite Swarms Block Astronomers Gaze
For millennia, bright lights sprinkled across our celestial sphere have guided great explorers, passed on storied traditions, and lent insight into the nature of our universe. Now, they have competition: thousands of satellites circling the globe in low orbit. Read the story: https://www.science.org/content/artic…
Front Covers: Nature Magazine – October 14
Science: Accupuncture’s Inflammation Effect, Antibiotics & Gut Bacteria
The neurons behind acupuncture’s effect on inflammation, and how antibiotics affect gut bacteria.
In this episode:
00:54 The neuronal basis for acupuncture’s effect on inflammation
In mice, electroacupuncture has been shown to reduce inflammation, but only when certain points on the body are stimulated. Why this is has puzzled scientists, but now, researchers have identified the specific neurons that are involved. They hope that this knowledge could be used in future to help treat certain inflammatory-related diseases.
Research article: Liu et al.
News and Views: Electroacupuncture activates neurons to switch off inflammation
07:28 Research Highlights
The Aztec origins of an obsidian ‘spirit mirror’, and the damage done by a Soviet plutonium complex.
Research Highlight: A ‘spirit mirror’ used in Elizabeth I’s court had Aztec roots
Research Highlight: Cold-war spy pictures reveal a Soviet nuclear ‘cloud generator’
10:18 Assessing antibiotics’ collateral damage.
Antibiotics are known to cause damage to the communities of bacteria that live in our guts. To better understand why this happens, a team has mapped the effects that different antibiotics have on individual gut-bacteria species, which may offer new insights into preventing this collateral damage.
Research article: Maier et al.
17:32 Briefing Chat
We discuss some highlights from the Nature Briefing. This time, the latest species to be declared extinct in the US, and a potential planet that orbits three stars.
New York Times: Protected Too Late: U.S. Officials Report More Than 20 Extinctions
New York Times: This May Be the First Planet Found Orbiting 3 Stars at Once