More than 360,000 people died from coronary artery disease in 2019. While there is no cure to the disease, you can take steps to lower your risk and manage the harmful plaque build-up impacting your health. The information in this video was accurate as of 11.25.2021 and is for information purposes only. Consult your local medical authority or your healthcare practitioner for advice.
Chapters: 0:00 Intro 0:12 What is coronary artery disease? 0:26 What are the signs of coronary artery disease? 0:41 Can you reverse coronary artery disease? 1:04 What are statins? 1:34 What are the treatments for coronary artery disease? 1:46 Make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk. 2:07 Taking medication can help treat coronary artery disease. 2:25 What is a coronary stent procedure? 3:03 What is coronary artery bypass graft surgery? 3:36 What’s the best treatment for coronary artery disease? 3:45 When should you talk to your doctor about coronary artery disease symptoms?





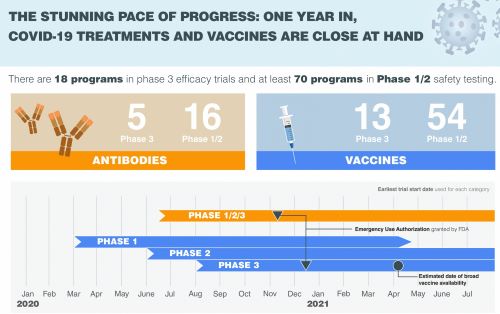
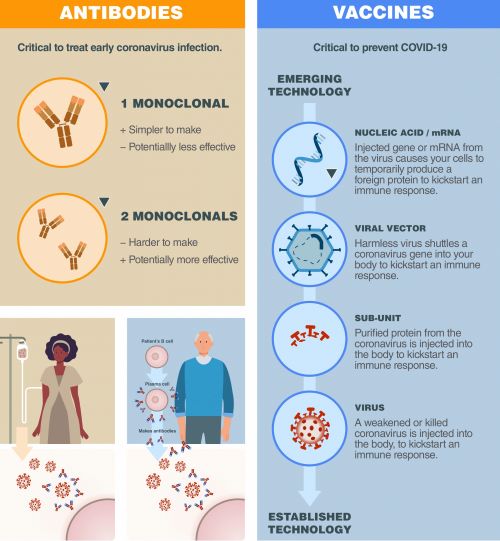




 Staff Writer Jon Cohen joins host Sarah Crespi to talk about using monoclonal antibodies to treat or prevent infection by SARS-CoV-2. Many companies and researchers are rushing to design and test this type of treatment, which proved effective in combating Ebola last year.
Staff Writer Jon Cohen joins host Sarah Crespi to talk about using monoclonal antibodies to treat or prevent infection by SARS-CoV-2. Many companies and researchers are rushing to design and test this type of treatment, which proved effective in combating Ebola last year. 


 Tension-type headaches can be either episodic or chronic. They are rarely disabling or associated with any significant autonomic phenomena, thus patients do not usually seek medical care and usually successfully self-treat. Unlike migraine, there is no significant nausea, no vomiting, and a lack of aggravation by routine physical activity.
Tension-type headaches can be either episodic or chronic. They are rarely disabling or associated with any significant autonomic phenomena, thus patients do not usually seek medical care and usually successfully self-treat. Unlike migraine, there is no significant nausea, no vomiting, and a lack of aggravation by routine physical activity.
 More than 6 million people worldwide have Parkinson disease. Even though it is classically associated with tremors, the disease has many manifestations and is very treatable for most patients.
More than 6 million people worldwide have Parkinson disease. Even though it is classically associated with tremors, the disease has many manifestations and is very treatable for most patients.