


From McKinsey & Company (July 9, 2020):
 The World Health Organization recently acknowledged that some evidence about in-room transmission is worrisome. In addition, after analyzing a transmission event at a restaurant in China, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) concluded that an asymptomatic patient transmitted the virus to families at two nearby tables.
The World Health Organization recently acknowledged that some evidence about in-room transmission is worrisome. In addition, after analyzing a transmission event at a restaurant in China, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) concluded that an asymptomatic patient transmitted the virus to families at two nearby tables.
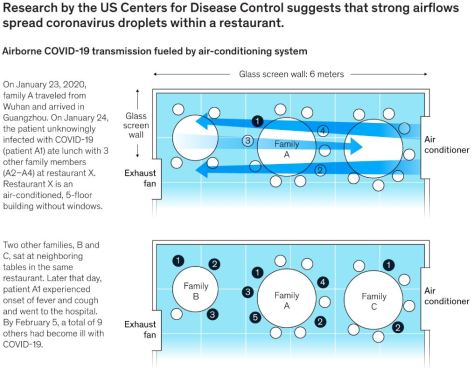
Based on the restaurant layout, seating arrangements, and smear samples from air-conditioning inlets and outlets, the CDC found that the coronavirus was likely transmitted when strong airflows from a nearby air conditioner spread large droplets from the infected person. These droplets traveled more than one meter—further than usual, but less than the distance aerosols can typically travel.


Diagnostics World (June 30, 2020): The shift from face-to-face patient visits to remote medical appointments is a worldwide phenomenon, but most especially in the U.S., finds a recent global survey conducted by the doctors-only social networking platform Sermo. Unsurprisingly, Zoom tops the list of most-mentioned technologies. About one-fifth of surveyed doctors say they expect to be using telehealth tools “significantly” more post-pandemic than before COVID-19 upended business as usual.
