
 His mission was to educate the world about the importance of sleep, which he believed was dangerously undervalued. His motto, “drowsiness is red alert,” is a message he tirelessly broadcast to his students, trainees, members of Congress and the world at large.
His mission was to educate the world about the importance of sleep, which he believed was dangerously undervalued. His motto, “drowsiness is red alert,” is a message he tirelessly broadcast to his students, trainees, members of Congress and the world at large.
William Dement, MD, PhD, known as the father of sleep medicine, died June 17 after a two-year battle with cardiovascular disease. He was 91.
 With a handful of other scientists, Dement, a longtime faculty member of the Stanford School of Medicine, created the fields of sleep research and sleep medicine, and his many books and lectures helped raise awareness of sleep disorders and the dangers of sleep deprivation.
With a handful of other scientists, Dement, a longtime faculty member of the Stanford School of Medicine, created the fields of sleep research and sleep medicine, and his many books and lectures helped raise awareness of sleep disorders and the dangers of sleep deprivation.
Dement’s many other accomplishments and accolades range far and wide: Dement and Guilleminault were the founding editors of the journal Sleep, the first major international journal devoted to sleep, publishing the first issue in 1978. He was the author of books for lay readers, including The Promise of Sleep, Some Must Watch While Some Must Sleep and The Sleepwatchers. The 2012 comedy film Sleepwalk with Me featured The Promise of Sleep and Dement in a cameo.



 “We’ve discovered that fragmented sleep is associated with a unique pathway — chronic circulating inflammation throughout the blood stream — which, in turn, is linked to higher amounts of plaques in coronary arteries,” said study senior author Matthew Walker, a UC Berkeley professor of psychology and neuroscience.
“We’ve discovered that fragmented sleep is associated with a unique pathway — chronic circulating inflammation throughout the blood stream — which, in turn, is linked to higher amounts of plaques in coronary arteries,” said study senior author Matthew Walker, a UC Berkeley professor of psychology and neuroscience.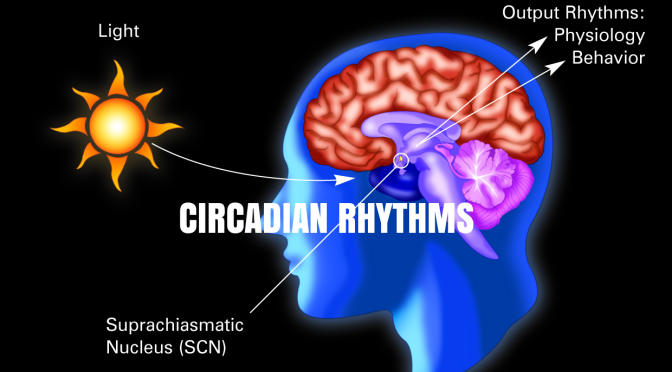
 By comparing the pancreatic cells of type 2 diabetic human donors with those of healthy people, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and at the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, were able to demonstrate, for the first time, that the pancreatic islet cells derived from the Type 2 Diabetic human donors bear compromised circadian oscillators.
By comparing the pancreatic cells of type 2 diabetic human donors with those of healthy people, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and at the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, were able to demonstrate, for the first time, that the pancreatic islet cells derived from the Type 2 Diabetic human donors bear compromised circadian oscillators. 

 When people are awake during the night, their behaviors are often mismatched with their internal body clocks. This can lead to nighttime eating, which can influence the way the body processes sugar and could lead to a higher risk in diabetes. “What happens when food is eaten when you normally should be fasting?” Scheer asked the audience. “What happens is that your glucose tolerance goes out the window….So your glucose levels after a meal are much higher.” This can increase people’s risk for diabetes.
When people are awake during the night, their behaviors are often mismatched with their internal body clocks. This can lead to nighttime eating, which can influence the way the body processes sugar and could lead to a higher risk in diabetes. “What happens when food is eaten when you normally should be fasting?” Scheer asked the audience. “What happens is that your glucose tolerance goes out the window….So your glucose levels after a meal are much higher.” This can increase people’s risk for diabetes.