What are some skywatching highlights in October 2020? Not one, but two, full moons; Mars at opposition; and finding the Andromeda galaxy.
Category Archives: Science
Top Science Podcasts: ‘Ice Loss In Greenland, Long-Covid & Whale Deep Dive

How current and future ice loss in Greenland compares to the past, Long-Covid, and using graphene to make ultra-sensitive radiation detectors.
In this episode:
00:45 Greenland’s historic ice loss
Climate change is accelerating the loss of ice and glaciers around the world leading to unprecedented levels of disappearance. Researchers have drilled samples from deep in the Greenland ice sheet, to model how current, and future, losses compare to those seen in the last 12,000 years. Research Article: Briner et al.; News and Views: The worst is yet to come for the Greenland ice sheet; Editorial: Arctic science cannot afford a new cold war
09:23 Coronapod
Despite recovering from an initial COVID-19 infection, many patients are experiencing severe symptoms months later. We find out about the impact of ‘Long Covid’ and the research that’s being done to try and understand it. News Feature: The lasting misery of coronavirus long-haulers
18:55 Research Highlights
A robot defeats humans at yet another sport, and extreme diving in Cuvier’s beaked whales. Research Highlight: A robot triumphs in a curling match against elite humans; Research Highlight: A smiling whale makes a record deep dive
21:20 A radiation detector made of graphene
Radiation-detectors known as bolometers are vital instruments in many fields of science. This week, two groups of researchers have harnessed graphene to make super sensitive bolometers that could be used to improve quantum computers, or detect subtle traces of molecules on other planets. Research Article: Lee et al.; Research Article: Kokkoniemi et al.
27:49 Briefing Chat
We discuss some of the latest stories highlighted in the Nature Briefing. This week we chat about the lack of diversity in academia, and an animal ally that can protect wildlife during forest fires. Nature Careers: Diversity in science: next steps for research group leaders; National Geographic:
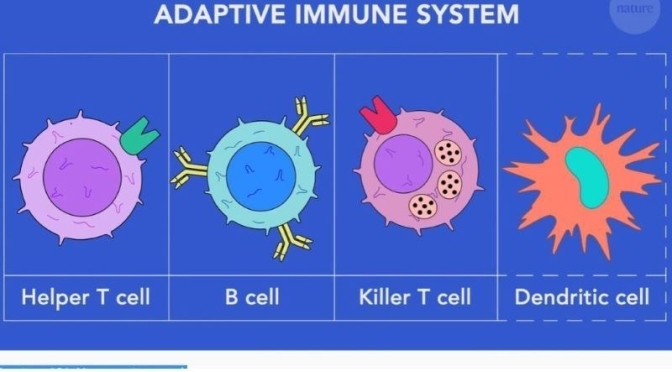
Health Videos: ‘How Vaccines Work With The Adaptive Immune System’
As the world waits for a potential COVID-19 vaccine, we delve into how vaccines actually work. What are the different types of vaccine? How do they trigger and train the immune system, and what is the role of herd immunity?
Top New Health Podcasts: ‘Flu Vaccine Season’ (BMJ)

With the annual flu season looming, GPs are anticipating a frenzy of vaccinations, perhaps more so than ever this year. As so many ‘flu and respiratory viruses circulate every year, and as the ‘flu vaccine is for one strain of influenza only, is the vaccine worth getting, and what are the risks associated with vaccinating vs. not vaccinating?
In this week’s episode, we discuss the high vaccine uptake in New Zealand, and the role that social distancing for COVID-19 may have played in their low numbers of seasonal flu. We also talk about whether or not the message we give to patients about the benefits and risks of vaccination is transparent enough, and how we might communicate better with them to allow them to make an informed decision. We feel pressure to increase vaccination rates, because we believe we are protecting people, but does the evidence support that?
Our guests: Nikki Turner is the director of the Immunisation Advisory Centre (IMAC) at the university of Auckland. She is an academic general practitioner, and a professor at the university. Jeff Kwong is a professor at the University of Toronto, and the interim director of the Centre for Vaccine Preventable Diseases at the university’s Dalla Lana School of Public Health. Newest Oldest Longest Shortest Random
TOP JOURNALS: RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS FROM SCIENCE MAGAZINE (SEPT 25, 2020)
Top Science Podcasts: 120,000 Year-Old Human Footprints, Neanderthal DNA ‘Y Chromosomes’

Contributing Correspondent Ann Gibbons talks with host Sarah Crespi about a series of 120,000-year-old human footprints found alongside prints from animals like asses, elephants, and camels in a dried-up lake on the Arabian Peninsula. These are the earliest human footprints found so far in Arabia and may help researchers better understand the history of early hominin migrations out of Africa.
Continuing on the history of humanity theme, Sarah talks with Janet Kelso of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, about her team’s efforts to fish the elusive Y chromosome out of Neanderthal and Denisovan DNA. It turns out Y chromosomes tell a different story about our past interbreeding with Neanderthals than previous tales told by the rest of the genome.
Top Science Podcasts: Plastic Diamond-Like Crystals, Rapid Antigen Tests & Stinging Trees

Nature reports on: Coaxing tiny colloid particles into a diamond structure, rapid antigen tests and manipulating cell death and homeostasis in neurodegenerative disease.
In this episode:
00:45 Creating colloidal crystals
For decades, researchers have attempted to create crystals with a diamond-like structure using tiny colloid particles. Now, a team thinks they’ve cracked it, which could open the door for new optical technologies. Research Article: He et al.
07:50 Coronapod
Rapid antigen tests for coronavirus have been described in some circles as ‘game changers’ in the fight against COVID-19. We discuss their strengths and weaknesses, and how they could fit into an overall testing strategy. News Feature: Fast coronavirus tests: what they can and can’t do; If you are involved in a clinical trial for a coronavirus vaccine or treatment, please fill in our survey.
23:52 Research Highlights
Climate change causes greening in the Arctic, and the peptide that gives the Giant Stinging Tree its sting. Research Highlight: A frozen land goes green as Earth warms; Research Highlight: How the giant stinging tree of Australia can inflict months of agony
26:04 Controlling cellular death
In neurodegenerative disease, cell death can be prevented, however this can lead to the accumulation of incorrectly folded proteins. Now researchers have found targets that can be used to both stop cell death and protein aggregation. Research Article: Xu et al.
32:20 Briefing Chat
We discuss some of the latest stories highlighted in the Nature Briefing. This week we talk about the increasing complexity of scientific writing, and uncovering the real origins of charcoal. Nature Index: Science is getting harder to read; Nature News: Microscopy illuminates charcoal’s sketchy origins
Top Interview Podcasts: Nobel Prize Geneticist Sir Paul Nurse – “What Is Life?”

In his new book, Paul Nurse, Nobel prize winner and director of the Francis Crick Institute, addresses a question that has long plagued both philosophers and scientists – what does it really mean to be alive?

Speaking to Madeleine Finlay, Paul delves into why it’s important to understand the underlying principles of life, the role of science in society, and what life might look like on other planets.
Sir Paul Maxime Nurse FRS FMedSci HonFREng HonFBA MAE, is an English geneticist, former President of the Royal Society and Chief Executive and Director of the Francis Crick Institute.
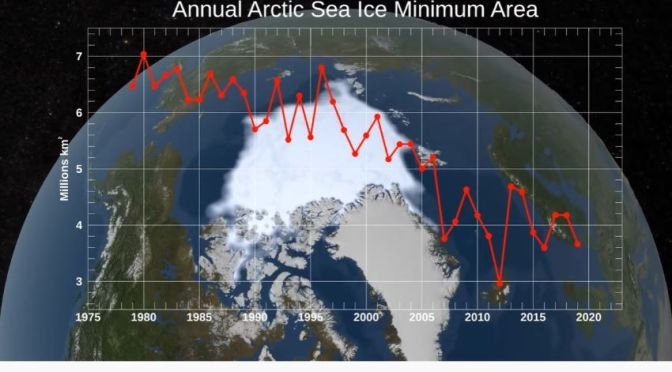
Environment Videos: NASA Reports Rising Arctic Temps, Low Sea Ice In 2020
On Sept. 15, 2020, Arctic sea ice reached its annual minimum extent — the second-lowest on record. This summer, temperatures soared in the Siberian Arctic, and intense fires burned through peatland. The Arctic region is warming three times faster than the rest of the planet.
Health: “The Science Of The Sun And Skin Cancer”

Melanoma may account for a small percentage of skin cancers, yet it causes an estimated 75 to 80 percent of skin cancer deaths. Caught early, it has a 99 percent five-year survival rate, but if it slips patients’ and clinicians’ notice, digs deeper into the skin and spreads beyond the lymph nodes, that rate can drop to 25 percent, according to the National Cancer Institute. The ACS predicts there will be 6,850 deaths in the United States from melanoma this year.
Although more skin pigment provides more protection, melanin itself has a sun protection factor, or SPF, of less than 5, says Fisher, suggesting that it functions physiologically as more than mere sunblock. He and others have clarified how different types of melanin raise or lower melanoma risk, and they’ve shown that any minimal benefit provided by tanning, such as the production of vitamin D, doesn’t outweigh the DNA damage caused by UV exposure.
Skin cancers are far and away the most common cancers in the United States. Basal and squamous cell carcinomas make up the vast majority, with somewhere between 1 million and 5.4 million new instances diagnosed each year. However, because these two malignancies don’t have to be reported to cancer registries, precise numbers aren’t known: The cancer officially ranked as the most common in this country is breast cancer, with 270,000 new cases each year. Melanoma is ranked fifth, with about 100,000 new diagnoses expected in 2020, reports the American Cancer Society (ACS).