A slight uptick in U.S. life expectancy in the U.S. in 2018 was due partly to a decrease in overdose deaths, but mostly to decreasing cancer deaths.
A slight uptick in U.S. life expectancy in the U.S. in 2018 was due partly to a decrease in overdose deaths, but mostly to decreasing cancer deaths.
From a BMJ online article:
We derived a healthy lifestyle score based on information on five lifestyle factors—diet, smoking, physical activity, alcohol consumption, and body mass index (BMI).
 Our findings suggest that promotion of a healthy lifestyle would help to reduce the healthcare burdens through lowering the risk of developing multiple chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, and extending disease-free life expectancy. Public policies for improving food and the physical environment conducive to adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle, as well as relevant policies and regulations (for example, smoking ban in public places or trans-fat restrictions), are critical to improving life expectancy, especially life expectancy free of major chronic diseases.
Our findings suggest that promotion of a healthy lifestyle would help to reduce the healthcare burdens through lowering the risk of developing multiple chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, and extending disease-free life expectancy. Public policies for improving food and the physical environment conducive to adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle, as well as relevant policies and regulations (for example, smoking ban in public places or trans-fat restrictions), are critical to improving life expectancy, especially life expectancy free of major chronic diseases.
The average life expectancy in the world has increased substantially in the past few decades. The aging of the population has led to a high prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Although people live longer, older individuals often live with disabilities and chronic diseases. People with chronic diseases including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes have a shorter life expectancy than do their peers without these chronic conditions. Estimates of the loss in life years due to these chronic conditions range from 7.5 to 20 years, depending on the methods used and the characteristics of the study population.
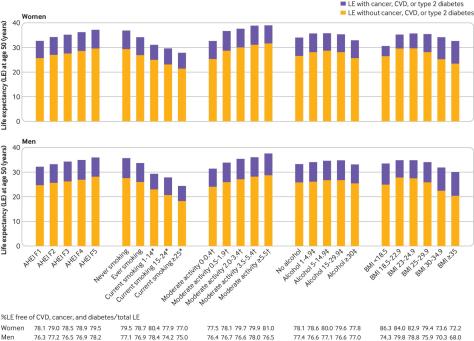
Modifiable lifestyle factors including smoking, physical activity, alcohol intake, body weight, and diet quality affect both total life expectancy and incidence of chronic diseases. Studies have shown that smoking, inactivity, poor diet quality, and heavy alcohol consumption contribute up to 60% of premature deaths and 7.4-17.9 years’ loss in life expectancy. Nevertheless, little research has looked at how a combination of multiple lifestyle factors may relate to life expectancy free from the major diseases of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.