nature Magazine – June 8, 2023 issue: Coral reef fishes, such as the blenny Ecsenius stictus pictured on the cover, are diverse, abundant and grow quickly. In this week’s issue, Alexandre Siqueira and his colleagues investigate the evolutionary history of these fishes to find out how growth has shaped life on coral reefs.
Camera that could fit on a penny captures vivid colour photos
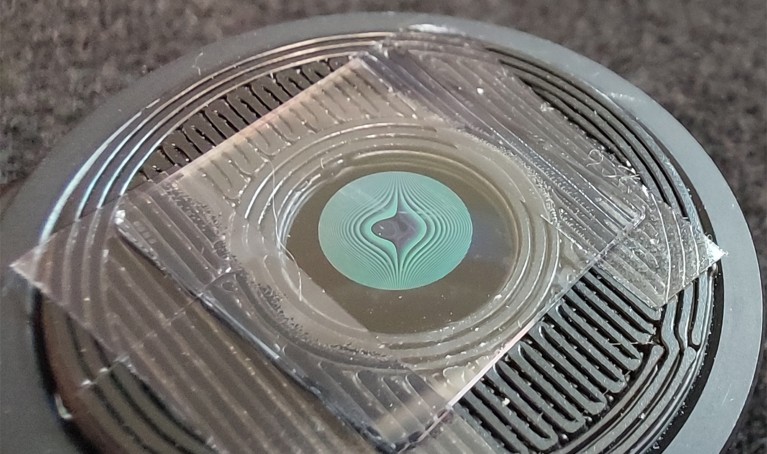

A ‘meta-lens’ and corrective algorithms allow a tiny device to produce high-resolution images.
A computational-imaging technique paves the way for ultra-small cameras that could be used in various portable devices.
These hardy ants build their own landmarks in the desert
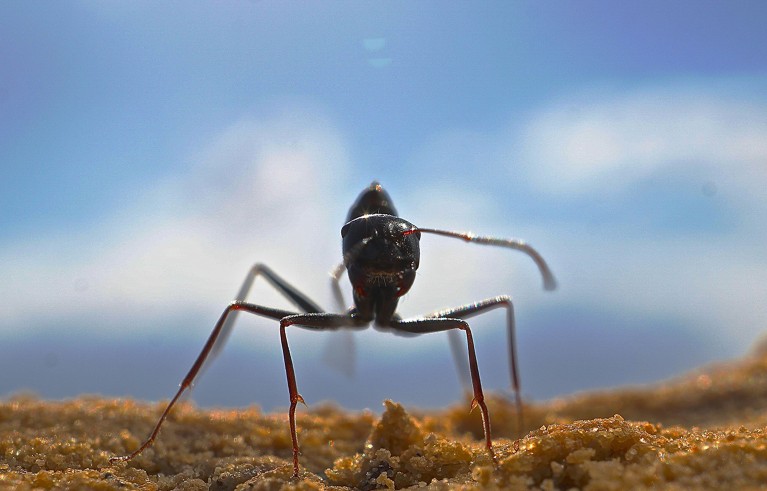

Ants living on the sprawling salt pans of Tunisia use DIY markers to find their way home.
The desert ant Cataglyphis fortis lives in Tunisia’s arid salt flats, and can travel more than a kilometre from its underground nest in search of food. Now scientists have found that these ants build tall hills on top of their nests that help the insects to find their way home across the vast, featureless landscape1.