Journal of the American Heart Association study (Feb 17, 2020):
 The association between poor overall sleep quality and greater consumption of added sugars observed in the current study aligns with previous findings that intakes of confectionary and sugar‐sweetened beverages were higher in middle‐aged Japanese women reporting poor, compared with good, sleep quality.
The association between poor overall sleep quality and greater consumption of added sugars observed in the current study aligns with previous findings that intakes of confectionary and sugar‐sweetened beverages were higher in middle‐aged Japanese women reporting poor, compared with good, sleep quality.
Background – Poor sleep increases cardiovascular disease risk, and diet likely contributes to this relationship. However, there are limited epidemiological data on the relationship between measures of sleep quality and habitual dietary patterns. This study examined these associations in a diverse sample of women.
Both short sleep duration and poor sleep quality are associated with the development of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease (CVD), and it is likely that the relationship between sleep and cardiometabolic disease risk is partially mediated by diet.5 Indeed, experimental studies demonstrate that restricting sleep duration leads to increases in energy intake, confirming associations of short sleep with higher energy intakes in observational population‐based studies.
Read full study
 “The decrease in people taking action to improve sleep is alarming, especially when it is clear people around the world deeply value sleep. Sleep deficit impacts people both mentally and physically, so we need to educate people on available sleep resources and empower them with the confidence that their efforts will pay off,” said Mark Aloia, PhD, Global Lead for Behavior Change, Sleep & Respiratory Care at Philips.
“The decrease in people taking action to improve sleep is alarming, especially when it is clear people around the world deeply value sleep. Sleep deficit impacts people both mentally and physically, so we need to educate people on available sleep resources and empower them with the confidence that their efforts will pay off,” said Mark Aloia, PhD, Global Lead for Behavior Change, Sleep & Respiratory Care at Philips.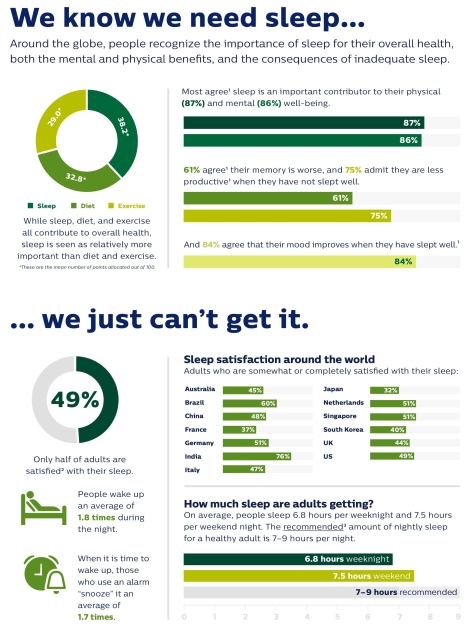

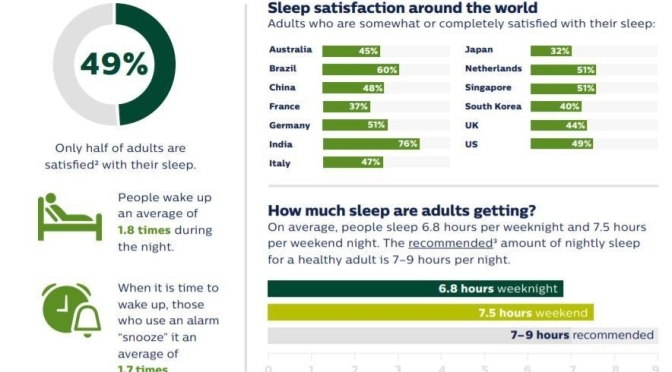

 The association between poor overall sleep quality and greater consumption of added sugars observed in the current study aligns with previous findings that intakes of confectionary and sugar‐sweetened beverages were higher in middle‐aged Japanese women reporting poor, compared with good, sleep quality.
The association between poor overall sleep quality and greater consumption of added sugars observed in the current study aligns with previous findings that intakes of confectionary and sugar‐sweetened beverages were higher in middle‐aged Japanese women reporting poor, compared with good, sleep quality.