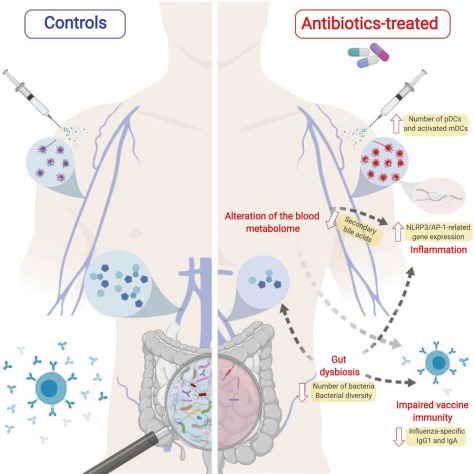
From a Neuroscience News & Research online article:
 “The link between antibiotic exposure and Parkinson’s disease fits the current view that in a significant proportion of patients the pathology of Parkinson’s may originate in the gut, possibly related to microbial changes, years before the onset of typical Parkinson motor symptoms such as slowness, muscle stiffness and shaking of the extremities. It was known that the bacterial composition of the intestine in Parkinson’s patients is abnormal, but the cause is unclear. Our results suggest that some commonly used antibiotics, which are known to strongly influence the gut microbiota, could be a predisposing factor,” says research team leader, neurologist Filip Scheperjans MD, Ph.D. from the Department of Neurology of Helsinki University Hospital.
“The link between antibiotic exposure and Parkinson’s disease fits the current view that in a significant proportion of patients the pathology of Parkinson’s may originate in the gut, possibly related to microbial changes, years before the onset of typical Parkinson motor symptoms such as slowness, muscle stiffness and shaking of the extremities. It was known that the bacterial composition of the intestine in Parkinson’s patients is abnormal, but the cause is unclear. Our results suggest that some commonly used antibiotics, which are known to strongly influence the gut microbiota, could be a predisposing factor,” says research team leader, neurologist Filip Scheperjans MD, Ph.D. from the Department of Neurology of Helsinki University Hospital.
Higher exposure to commonly used oral antibiotics is linked to an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease according to a recently published study by researchers from the Helsinki University Hospital, Finland.
The strongest associations were found for broad-spectrum antibiotics and those that act against anaerobic bacteria and fungi. The timing of antibiotic exposure also seemed to matter.
The study suggests that excessive use of certain antibiotics can predispose to Parkinson’s disease with a delay of up to 10 to 15 years. This connection may be explained by their disruptive effects on the gut microbial ecosystem.



 Benjamin Thompson brings you the latest science news. This week, an antibiotic that targets difficult to treat bacteria, and a roundup of the latest science news.
Benjamin Thompson brings you the latest science news. This week, an antibiotic that targets difficult to treat bacteria, and a roundup of the latest science news.
 More than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur in the United States each year, and more than 35,000 people die as a result. In addition, nearly 223,900 people in the United States required hospital care for C. difficile and at least 12,800 people died in 2017.
More than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur in the United States each year, and more than 35,000 people die as a result. In addition, nearly 223,900 people in the United States required hospital care for C. difficile and at least 12,800 people died in 2017.
 The top 10 most commonly administered antibiotics in the ER for nonadmitted patients were:
The top 10 most commonly administered antibiotics in the ER for nonadmitted patients were:
 At Dr. Soong’s hospital, withholding the results of urine cultures, unless doctors actually called the microbiology lab to request them,
At Dr. Soong’s hospital, withholding the results of urine cultures, unless doctors actually called the microbiology lab to request them,