From a Science Magazine online article:
Antibiotic use diminished the gut microbiome composition and impaired the ability of the immune system to generate antibodies. Treatment with antibiotics also disturbed bile acid metabolism and caused inflammatory responses.
From the original findings the Journal “Cell.com”:
Emerging evidence indicates a central role for the microbiome in immunity. However, causal evidence in humans is sparse. Here, we administered broad-spectrum antibiotics to healthy adults prior and subsequent to seasonal influenza vaccination. Despite a 10,000-fold reduction in gut bacterial load and long-lasting diminution in bacterial diversity, antibody responses were not significantly affected. However, in a second trial of subjects with low pre-existing antibody titers, there was significant impairment in H1N1-specific neutralization and binding IgG1 and IgA responses.
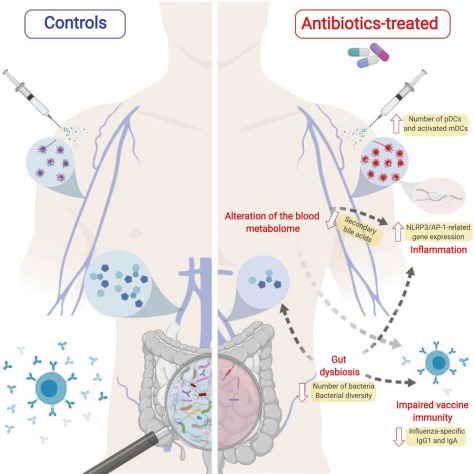
In addition, in both studies antibiotics treatment resulted in (1) enhanced inflammatory signatures (including AP-1/NR4A expression), observed previously in the elderly, and increased dendritic cell activation; (2) divergent metabolic trajectories, with a 1,000-fold reduction in serum secondary bile acids, which was highly correlated with AP-1/NR4A signaling and inflammasome activation. Multi-omics integration revealed significant associations between bacterial species and metabolic phenotypes, highlighting a key role for the microbiome in modulating human immunity.



 In summary, dietary fructose, but not glucose, supplementation of HFD impairs mitochondrial size, function, and protein acetylation, resulting in decreased fatty acid oxidation and development of metabolic dysregulation.
In summary, dietary fructose, but not glucose, supplementation of HFD impairs mitochondrial size, function, and protein acetylation, resulting in decreased fatty acid oxidation and development of metabolic dysregulation.
 “As a result, today’s epidemic of physical inactivity in conjunction with highly processed, high-sodium diets contributes to thicker, stiffer hearts that compromise the heart’s ability to cope with endurance physical activity, and importantly this may start to occur prior to increases in resting blood pressure,” explains Shave.
“As a result, today’s epidemic of physical inactivity in conjunction with highly processed, high-sodium diets contributes to thicker, stiffer hearts that compromise the heart’s ability to cope with endurance physical activity, and importantly this may start to occur prior to increases in resting blood pressure,” explains Shave. …a new
…a new 
 There may be no easy fix for the loneliness epidemic plaguing the nation, but helping people cope with hearing loss could be one key to tackling this complex problem. Hearing loss affects 1 of every 5 people and is strongly linked to loneliness: Every decibel drop in perception in people under 70 increases the odds of becoming severely lonely by 7%,
There may be no easy fix for the loneliness epidemic plaguing the nation, but helping people cope with hearing loss could be one key to tackling this complex problem. Hearing loss affects 1 of every 5 people and is strongly linked to loneliness: Every decibel drop in perception in people under 70 increases the odds of becoming severely lonely by 7%, 
 …the optimal strategy when faced with two propositions is to sum up the values associated with the memories you have of each choice, then calculate the difference between these two sums (do I have more positive memories linked to chocolate eclairs or macaroons?). The decision is made when this difference reaches a threshold value, fixed in advance, which determines the time taken in making the decision. This model leads to rapid decision-making when the values of the two possibilities are very far apart. But when two choices have almost the same value, we need more time, because we need to draw on more memories so that this difference reaches the decision threshold.
…the optimal strategy when faced with two propositions is to sum up the values associated with the memories you have of each choice, then calculate the difference between these two sums (do I have more positive memories linked to chocolate eclairs or macaroons?). The decision is made when this difference reaches a threshold value, fixed in advance, which determines the time taken in making the decision. This model leads to rapid decision-making when the values of the two possibilities are very far apart. But when two choices have almost the same value, we need more time, because we need to draw on more memories so that this difference reaches the decision threshold. Our findings suggest that higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with better cognitive performance, and therefore less cognitive decline, in older but not middle-aged individuals.
Our findings suggest that higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with better cognitive performance, and therefore less cognitive decline, in older but not middle-aged individuals.
 “Remote procedures have the potential to transform how we deliver care when treating the most time-sensitive illnesses such as heart attack and stroke. The success of this study paves the way for large-scale, long-distance telerobotic platforms across the globe, and its publication in Lancet’s EClinicalMedicine demonstrates the transformative nature of telerobotics,”
“Remote procedures have the potential to transform how we deliver care when treating the most time-sensitive illnesses such as heart attack and stroke. The success of this study paves the way for large-scale, long-distance telerobotic platforms across the globe, and its publication in Lancet’s EClinicalMedicine demonstrates the transformative nature of telerobotics,” 
 The team found 85% of people first diagnosed with dementia were diagnosed by a non-dementia specialist physician, usually a primary care doctor, and an “unspecified dementia” diagnosis was common.
The team found 85% of people first diagnosed with dementia were diagnosed by a non-dementia specialist physician, usually a primary care doctor, and an “unspecified dementia” diagnosis was common.
 In our study, we found significant associations between baseline teeth symptoms and change in episodic memory. Deficits in episodic memory (ie, ability to retain new information) are most common in older adults with mild cognitive impairment making them more likely to progress to Alzheimer’s disease dementia.
In our study, we found significant associations between baseline teeth symptoms and change in episodic memory. Deficits in episodic memory (ie, ability to retain new information) are most common in older adults with mild cognitive impairment making them more likely to progress to Alzheimer’s disease dementia.