The race between covid-19 vaccines and variants is on. Alok Jha, The Economist’s science correspondent, and Natasha Loder, health policy editor, discuss what this means for the future Read more of our coverage on coronavirus: https://econ.st/3t1L6wx
Tag Archives: Medicine
Analysis: Why Pharmacies Are Overpriced (CNBC)
Concerns over prescription drug prices have grown into a big political issue, with nearly one in four Americans saying it’s difficult to afford their medications, according to a March 2019 poll by the Kaiser Family Foundation. Pharmacies technically set their own prices for generic drugs, but there are other players involved that complicate the process. Here’s how the system works and what customers can do to save money.
Chapters 0:00 – Introduction 1:16 – Why pharmacies exist 3:50 – How pharmacies make money 8:51 – Regulations 10:55 – How customers can save money
Covid-19: Patients Dying In Name Of Vaccine Freedom
In the video above, Alexander Stockton, a producer on the Opinion Video team, explores two of the main reasons the number of Covid cases is soaring once again in the United States: vaccine hesitancy and refusal. “It’s hard to watch the pandemic drag on as Americans refuse the vaccine in the name of freedom,” he says. Seeking understanding, Mr. Stockton travels to Mountain Home, Ark., in the Ozarks, a region with galloping contagion and — not unrelated — abysmal vaccination rates. He finds that a range of feelings and beliefs underpins the low rates — including fear, skepticism and a libertarian strain of defiance. This doubt even extends to the staff at a regional hospital, where about half of the medical personnel are not vaccinated — even while the intensive care unit is crowded with unvaccinated Covid patients fighting for their lives. Mountain Home — like the United States as a whole — is caught in a tug of war between private liberty and public health. But Mr. Stockton suggests that unless government upholds its duty to protect Americans, keeping the common good in mind, this may be a battle with no end.
Health: Looking Out For Diverticulitis (Harvard)
Covid-19: What To Know About Booster Shots (WSJ)
The Biden administration announced that Americans who have been fully vaccinated with a two-dose regimen against Covid-19 should receive a booster, citing the threat from the highly contagious Delta variant. WSJ breaks down what you need to know. Photo: Kamil Krzaczynski/Reuters
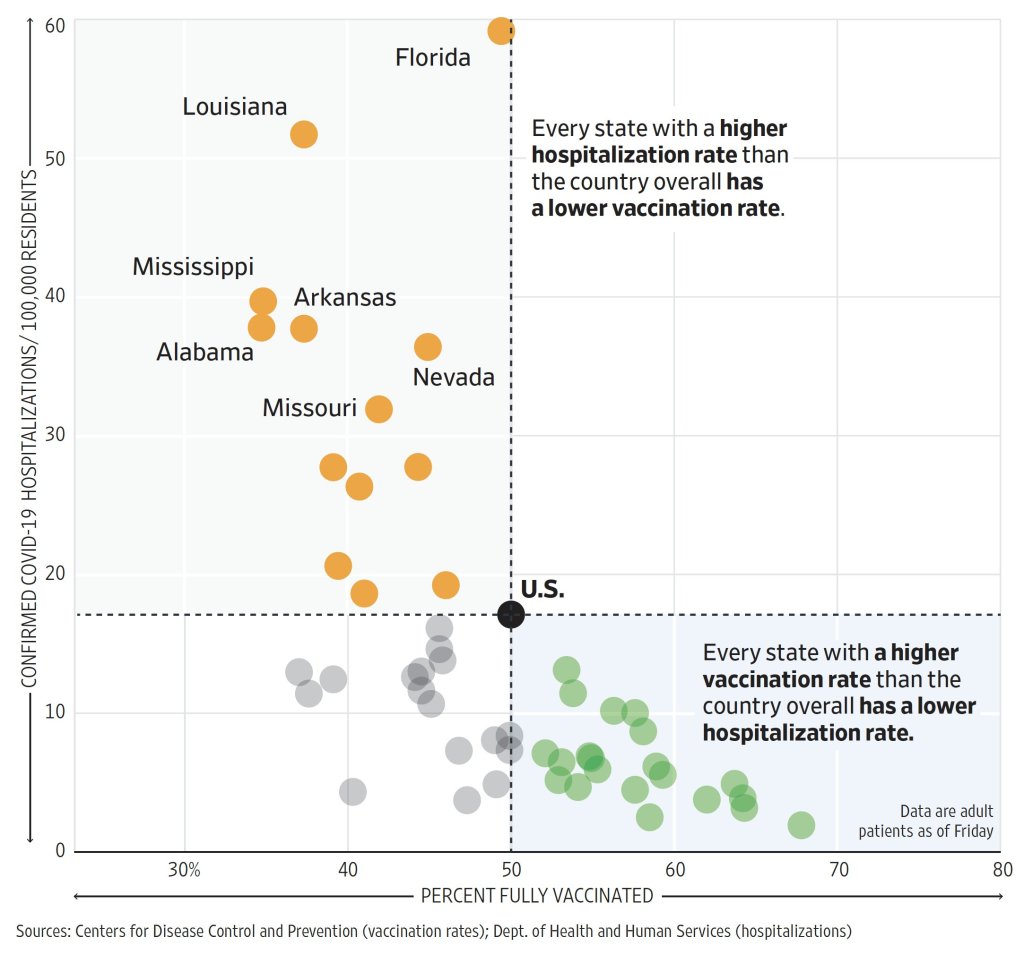
COVID-19 INFOGRAPHIC: U.S. VACCINATION RATES & STATES HOSPITALIZATIONS (AUG 9)
Highly Vaccinated States Keep Worst Covid-19 Outcomes in Check as Delta Spreads, WSJ Analysis Shows
Medicine: Transcatheter Treatments For Valvular Heart Disease (JAMA Video)
Transcatheter valvular repair and implantation has become increasingly common for treating patients diagnosed with valvular heart diseases.
0:00 This video summarizes the three transcatheter valvular therapies currently in use in the United States: transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI), transcatheter valve-in-valve procedures, and transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral valve repair.
0:47 Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVI) for patients with severe aortic stenosis regardless of surgical risk 2:47 Transcatheter valve-in-valve procedures for patients with bioprosthetic valve failure
3:35 Transcatheter mitral valve repair for high surgical risk degenerative mitral regurgitation and for severe functional mitral regurgitation regardless of surgical risk.
Cover Stories: Newsweek – ‘The Doomsday Variant’
Medicine: Understanding ‘Long Covid’ Syndrome
Depression: How Ketamine Can Help (Yale Medicine)
Depression is one of the most common and most debilitating mental health disorders, affecting some 17 million adults in the US. It also continues to be a misunderstood, often hard-to-treat illness. Researchers have worked for decades to better understand the neurobiology underpinning depression.
For patients with severe, treatment-resistant depression, spending months or even years searching for good treatments can be totally disabling. The prevailing hypothesis for years was that depression was regulated by the neurotransmitter’s serotonin and norepinephrine.
Eventually, data began to suggest that maybe something much larger and more global was involved in the brain to account for depression, which led researchers to begin working with glutamate and GABA, the most abundant neurotransmitters in the brain. These chemicals are involved in neuroplasticity – the brain’s ability to adapt to change and protect itself against stressful events.
Neuroplasticity is a physical thing, too: it manifests itself “in terms of synapses, how these neurons are actually touching each other and communicating with each other,” explains Gerard Sanacora, PhD, MD, Director of the Yale Depression Research Program. “And we know that in depression, the number and strength of these interconnections decreases,” says Rachel Katz, MD, a professor of Clinical Psychiatry at Yale.
Ketamine – originally developed and still used as an anesthetic – works on those two neurotransmitters and was discovered to have rapid antidepressant effects. Some experience an improvement in symptoms in 24 hours or less. “We think that one of the things that Ketamine does, that helps to explain its antidepressant effects, is help the brain to regrow the synapses, the connections between nerve cells,” says John Krystal, MD, Chair of the Department of Psychiatry at Yale.