Although intermittent fasting is most widely known as a weight-loss strategy, emerging research suggests that it could have benefits for brain health and cognition. But does it actually work, are there any drawbacks and how long would you have to fast to see benefits? WSJ’s Daniela Hernandez breaks down what’s known and what’s not about the neuroscience of intermittent fasting.
Timeline: 0:00 Could intermittent fasting help our brains work better and longer? 0:31 How long would you have to fast to see any potential cognitive benefits? 1:04 How intermittent fasting could affect your ability to focus 2:27 Potential mood-related benefits of intermittent fasting 2:48 How intermittent fasting can affect brain health 4:03 Potential drawbacks of intermittent fasting


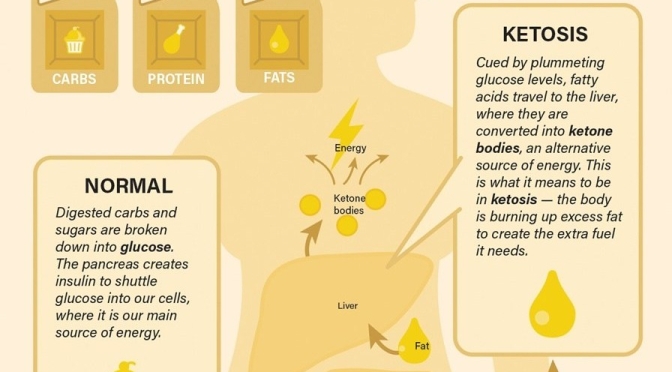
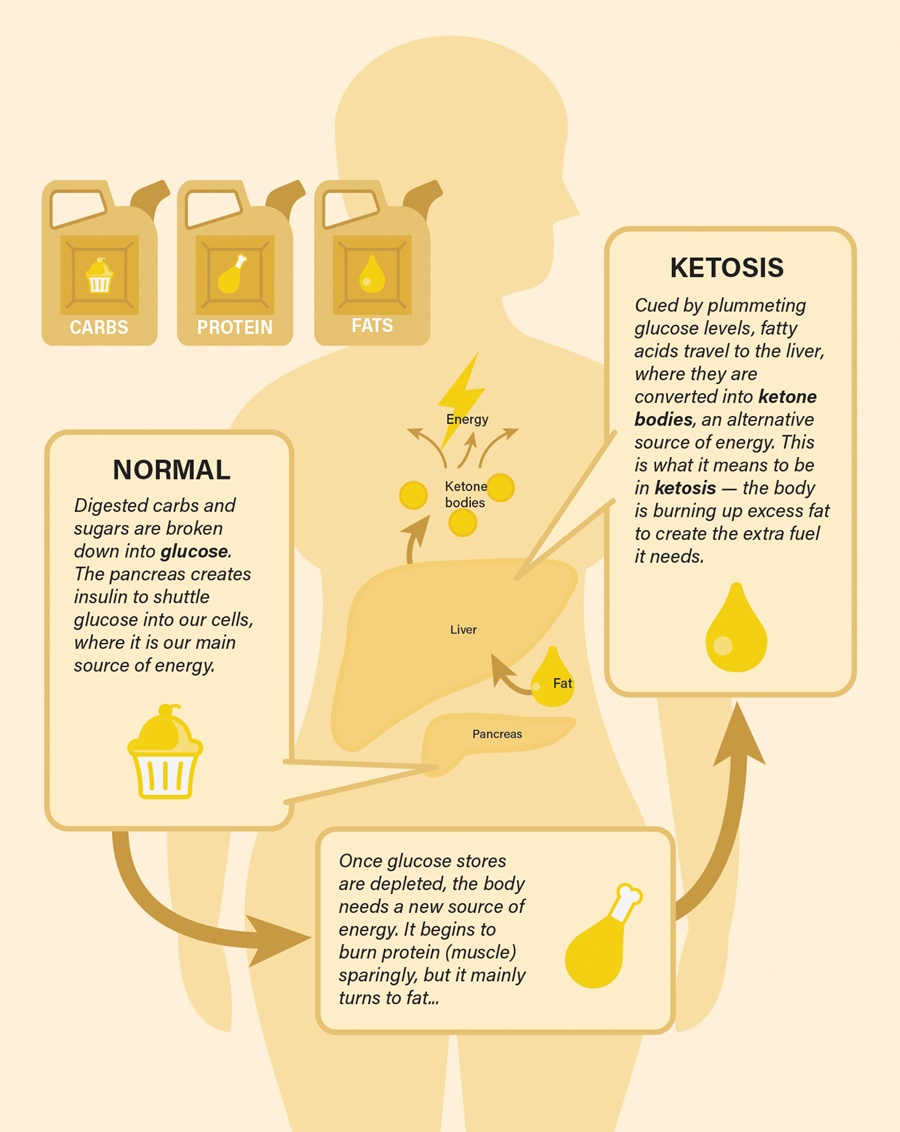
 to a paper Mattson and colleagues published in February in the experimental biology journal FASEB. In humans, fasting for 12 hours or more drops the levels of glycogen, a form of cellular glucose. Like changing to a backup gas tank, the body switches from glucose to fatty acids, a more efficient fuel. The switch generates the production of ketones, which are energy molecules that are made in the liver. “When the fats are mobilized and used to produce ketones, we think that is a key factor in accruing the health benefits,” says Mattson.
to a paper Mattson and colleagues published in February in the experimental biology journal FASEB. In humans, fasting for 12 hours or more drops the levels of glycogen, a form of cellular glucose. Like changing to a backup gas tank, the body switches from glucose to fatty acids, a more efficient fuel. The switch generates the production of ketones, which are energy molecules that are made in the liver. “When the fats are mobilized and used to produce ketones, we think that is a key factor in accruing the health benefits,” says Mattson.