The U.S. began vaccinating the population against the coronavirus earlier this month, but mass adoption is not a guarantee. Roughly four in ten Americans say they would “definitely” or “probably” not get a vaccine, according to a recent survey by the Pew Research Center. Watch this video to find out how major stakeholders plan to convince the entire country to trust a vaccine made in record time, using mRNA technology that’s never before been licensed.
Tag Archives: Herd Immunity
New Science Podcast: Lab-Grown Mini Brains, Herd Immunity & Bat Dinosaurs

The chances of mini brains becoming sentient, herd immunity, bat-like dinosaurs, and a UK government decision threatens gender diversity in academia.
In this episode:
00:59 The ethics of creating consciousness
Brain organoids, created by culturing stem cells in a petri dish, are a mainstay of neuroscience research. But as these mini-brains become more complex, is there the chance they could become conscious, and if so, how could we tell?
News Feature: Can lab-grown brains become conscious?
09:01 Coronapod
So called ‘herd immunity’ is claimed by some as a way to break the chain of infection and curtail the pandemic. However epidemiologists say that this course of action is ineffective and will lead to large numbers of infections and deaths.
News Explainer: The false promise of herd immunity for COVID-19
20:59 Research Highlights
Volcanic ash degrades ancient art in Pompeii, and the aerial ineptitude of two bat-like dinosaurs.
Research Highlight: The volcanic debris that buried Pompeii wreaks further destruction; Research Highlight: A dead end on the way to the sky
23:22 How cutting red-tape could harm gender diversity in UK academia
The Athena SWAN scheme, designed to boost gender-equality in UK academia, has proved effective, and has been exported to countries around the world. But now a decision by the UK government to cut bureaucracy could mean that institutions pay less heed to schemes like this and threaten future efforts to increase gender diversity in UK academia.
Editorial: Equality and diversity efforts do not ‘burden’ research — no matter what the UK government says
31:00 Briefing Chat
We discuss some highlights from the Nature Briefing. This time, oncologists discover a potential new human organ, and how re-examined fossils have given new insights into the size of baby tyrannosaurs.
Infographic: ‘What Is Herd Immunity?’ – Achieving It With Covid-19 (JAMA)
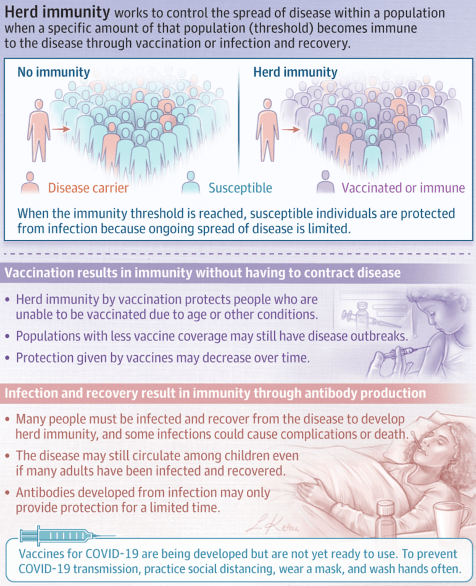

What Is Herd Immunity?
Herd immunity occurs when a significant portion of a population becomes immune to an infectious disease, limiting further disease spread.
Disease spread occurs when some proportion of a population is susceptible to the disease. Herd immunity occurs when a significant portion of a population becomes immune to an infectious disease and the risk of spread from person to person decreases; those who are not immune are indirectly protected because ongoing disease spread is very small.
The proportion of a population who must be immune to achieve herd immunity varies by disease. For example, a disease that is very contagious, such as measles, requires more than 95% of the population to be immune to stop sustained disease transmission and achieve herd immunity.
How Is Herd Immunity Achieved?
Herd immunity may be achieved either through infection and recovery or by vaccination. Vaccination creates immunity without having to contract a disease. Herd immunity also protects those who are unable to be vaccinated, such as newborns and immunocompromised people, because the disease spread within the population is very limited. Communities with lower vaccine coverage may have outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases because the proportion of people who are vaccinated is below the necessary herd immunity threshold. In addition, the protection offered by vaccines may wane over time, requiring repeat vaccination.
Achieving herd immunity through infection relies on enough people being infected with the disease and recovering from it, during which they develop antibodies against future infection. In some situations, even if a large proportion of adults have developed immunity after prior infection, the disease may still circulate among children. In addition, antibodies from a prior infection may only provide protection for a limited duration.
People who do not have immunity to a disease may still contract an infectious disease and have severe consequences of that disease even when herd immunity is very high. Herd immunity reduces the risk of getting a disease but does not prevent it for nonimmune people.
Herd Immunity and COVID-19
There is no effective vaccine against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) yet, although several are currently in development. It is not yet known if having this disease confers immunity to future infection, and if so, for how long. A large proportion of people would likely need to be infected and recover to achieve herd immunity; however, this situation could overwhelm the health care system and lead to many deaths and complications. To prevent disease transmission, keep distance between yourself and others, wash your hands often with soap and water or sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol, and wear a face covering in public spaces where it is difficult to avoid close contact with others.
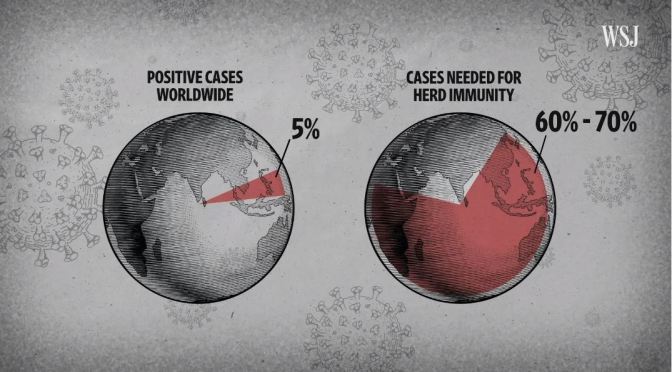
Coronavirus: “What It Will Take To Reach Herd Immunity” (WSJ Video)
Scientists are working at breakneck speed to develop an effective vaccine for the coronavirus. Their ultimate goal: to immunize enough of the world’s population to reach herd immunity. WSJ explains.
Illustration: Jacob Reynolds
Morning News Podcast: Federal Agents, Herd Immunity & Public Lands
 NPR News reports on Federal Agents being sent to states to stem violent crime, Covid-19 and the possibilities for ‘natural herd immunity, federal funding for public lands and more.
NPR News reports on Federal Agents being sent to states to stem violent crime, Covid-19 and the possibilities for ‘natural herd immunity, federal funding for public lands and more.