From a Smart Cities Dive online opinion article;
 The reality, however, is that modular, prefabricated housing can exceed the limitations put upon it by popular conceptions of trailer parks and postwar government housing. Not only are they certainly faster – an important factor in cost, as the cost of land and construction have as much as doubled in some parts of America within the past decade – but also of a higher quality.
The reality, however, is that modular, prefabricated housing can exceed the limitations put upon it by popular conceptions of trailer parks and postwar government housing. Not only are they certainly faster – an important factor in cost, as the cost of land and construction have as much as doubled in some parts of America within the past decade – but also of a higher quality.
Looking toward the expected lifespan of these homes, due to the precision of factory construction and the availability of new materials, some prefab or modular homes have the potential to even outlast traditionally-built, on-site housing.
A far cry from the “prefabs” of the 1950s, modules can be manufactured off-site in factories, in a cutting edge process of designing and building homes that can drive real change in an industry that has seen little change in centuries. Modular manufacturing permits us to get down to a level of detail and robustness that traditional architects, structural engineers and mechanical and electrical engineering consultants do not normally go into.
To read more: https://www.smartcitiesdive.com/news/affordable-housing-shortage-highlights-the-need-for-construction-to-enter-t/568435/



 Most notable is Toogood’s sensitive approach to materials. She offers two different, equally alluring solutions to the exterior cladding and the internal finishes. Both external cladding options, raw galvanised steel and dark charred timber, are suggestive of industrial or agricultural structures, making it something of a thrill to see them in a domestic setting. The building clad in raw galvanised steel will have a refined, cream-coloured interior, whilst the structure clad in dark charred timber will have an exposed plywood interior finish.
Most notable is Toogood’s sensitive approach to materials. She offers two different, equally alluring solutions to the exterior cladding and the internal finishes. Both external cladding options, raw galvanised steel and dark charred timber, are suggestive of industrial or agricultural structures, making it something of a thrill to see them in a domestic setting. The building clad in raw galvanised steel will have a refined, cream-coloured interior, whilst the structure clad in dark charred timber will have an exposed plywood interior finish.
 This model is going to be completely off-grid in its seaside location. On the roof are 6 x Trina 270w Honey Poly Module panels. A storage box over the tow bar stores the inverter and 4 x C&D 12V 192Ah c20 FT Lead Carbon Cyclic Batteries that will power the home. A new feature in this home (requested by the client) was a folding shelf in the bathroom above the toilet.
This model is going to be completely off-grid in its seaside location. On the roof are 6 x Trina 270w Honey Poly Module panels. A storage box over the tow bar stores the inverter and 4 x C&D 12V 192Ah c20 FT Lead Carbon Cyclic Batteries that will power the home. A new feature in this home (requested by the client) was a folding shelf in the bathroom above the toilet. 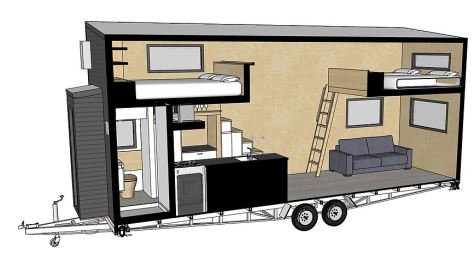

 “If one imagines a list of the greatest, most influential houses of the twentieth century, it seems highly likely that the mid-century period will dominate,” writes Bradbury in the book’s introduction, going on to name such famous edifices as the three famous glass houses by Philip Johnson, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, and Lino Bo Bardi, respectively; Richard Neutra’s Kaufmann House; and Luis Barragán’s Cuadra San Cristóbal. “One could, of course, go on.…” he writes.
“If one imagines a list of the greatest, most influential houses of the twentieth century, it seems highly likely that the mid-century period will dominate,” writes Bradbury in the book’s introduction, going on to name such famous edifices as the three famous glass houses by Philip Johnson, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, and Lino Bo Bardi, respectively; Richard Neutra’s Kaufmann House; and Luis Barragán’s Cuadra San Cristóbal. “One could, of course, go on.…” he writes.

 The Home Upgrade looks beyond big budget projects and explores homes where the seemingly impossible has been achieved. For architects striking out on their own, such projects offer the opportunity to flex their muscles and lead a project for the first time. A home in Brooklyn, featured in the book, was refurbished after Hurricane Sandy ravaged the Eastern Seaboard in 2012. The living space was raised above the high-water line, an answer to the grim fact that once-in-a-generation occurrences are a new reality.
The Home Upgrade looks beyond big budget projects and explores homes where the seemingly impossible has been achieved. For architects striking out on their own, such projects offer the opportunity to flex their muscles and lead a project for the first time. A home in Brooklyn, featured in the book, was refurbished after Hurricane Sandy ravaged the Eastern Seaboard in 2012. The living space was raised above the high-water line, an answer to the grim fact that once-in-a-generation occurrences are a new reality.
 The idea for this ADU was conceived in the wake of the 2018 Woolsey Fire, as a way to help families reinhabit their properties while rebuilding their primary residence. All “BUD” designs provide beautiful living spaces that can be delivered quickly and enjoyed for generations as a valuable addition to almost any property.
The idea for this ADU was conceived in the wake of the 2018 Woolsey Fire, as a way to help families reinhabit their properties while rebuilding their primary residence. All “BUD” designs provide beautiful living spaces that can be delivered quickly and enjoyed for generations as a valuable addition to almost any property.


 Two containers make up the ground floor of each house, with two more cantilevered three metres over one end to create a sheltered porch below and a first-floor terrace off the master bedroom.
Two containers make up the ground floor of each house, with two more cantilevered three metres over one end to create a sheltered porch below and a first-floor terrace off the master bedroom. Squirrel Park is a scheme of four houses made from converted shipping containers in Oklahoma City,
Squirrel Park is a scheme of four houses made from converted shipping containers in Oklahoma City, 
 Cork House embodies a strong whole life approach to sustainability, from resource through to end-of-life. Expanded cork is a pure bio-material made with waste from cork forestry. The bark of the cork oak is harvested by hand every nine years without harming the tree or disturbing the forest.
Cork House embodies a strong whole life approach to sustainability, from resource through to end-of-life. Expanded cork is a pure bio-material made with waste from cork forestry. The bark of the cork oak is harvested by hand every nine years without harming the tree or disturbing the forest.  This gentle agro-industry sustains the Mediterranean cork oak landscapes, providing a rich biodiverse habitat that is widely recognised. This compelling ecological origin of expanded cork is mirrored at the opposite end of the building’s lifecycle. The construction system is dry-jointed, so that all 1,268 blocks of cork can be reclaimed at end-of-building-life for re-use, recycling, or returning to the biosphere.
This gentle agro-industry sustains the Mediterranean cork oak landscapes, providing a rich biodiverse habitat that is widely recognised. This compelling ecological origin of expanded cork is mirrored at the opposite end of the building’s lifecycle. The construction system is dry-jointed, so that all 1,268 blocks of cork can be reclaimed at end-of-building-life for re-use, recycling, or returning to the biosphere.