In December 2020, a week before cardiologist Stuart Katz was scheduled to receive his first COVID-19 vaccine, he came down with a fever. He spent the next two weeks wracked with a cough, body aches and chills. After months of helping others to weather the pandemic, Katz, who works at New York University, was having his own first-hand experience of COVID-19.
On Christmas Day, Katz’s acute illness finally subsided. But many symptoms lingered, including some related to the organ he’s built his career around: the heart. Walking up two flights of stairs would leave him breathless, with his heart racing at 120 beats per minute. Over the next several months, he began to feel better, and he’s now back to his normal routine of walking and cycling. But reports about COVID-19’s effects on the cardiovascular system have made him concerned about his long-term health. “I say to myself, ‘Well, is it really over?’” Katz says.
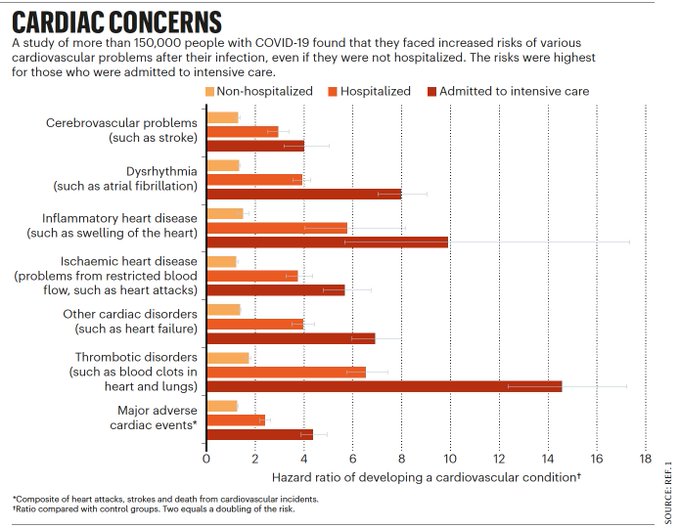
In one study1 this year, researchers used records from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) to estimate how often COVID-19 leads to cardiovascular problems. They found that people who had had the disease faced substantially increased risks for 20 cardiovascular conditions — including potentially catastrophic problems such as heart attacks and strokes — in the year after infection with the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Researchers say that these complications can happen even in people who seem to have completely recovered from a mild infection.
Some smaller studies have mirrored these findings, but others find lower rates of complications. With millions or perhaps even billions of people having been infected with SARS-CoV-2, clinicians are wondering whether the pandemic will be followed by a cardiovascular aftershock. Meanwhile, researchers are trying to understand who is most at risk of these heart-related problems, how long the risk persists and what causes these symptoms.




 “For patients with severe but stable heart disease who don’t want to undergo these invasive procedures, these results are very reassuring,” said
“For patients with severe but stable heart disease who don’t want to undergo these invasive procedures, these results are very reassuring,” said 
 In people having lack of Vitamin D, the muscle strength of waist, back, neck decreases. Decreased muscle strength can cause herniated disc and cervical discal hernia. All of this is reflected in the patient’s pain. We wanted to pay attention to the necessity of considering the lack of Vitamin D in low back pain (LBP) which is one of the common complaints of our patients.
In people having lack of Vitamin D, the muscle strength of waist, back, neck decreases. Decreased muscle strength can cause herniated disc and cervical discal hernia. All of this is reflected in the patient’s pain. We wanted to pay attention to the necessity of considering the lack of Vitamin D in low back pain (LBP) which is one of the common complaints of our patients.