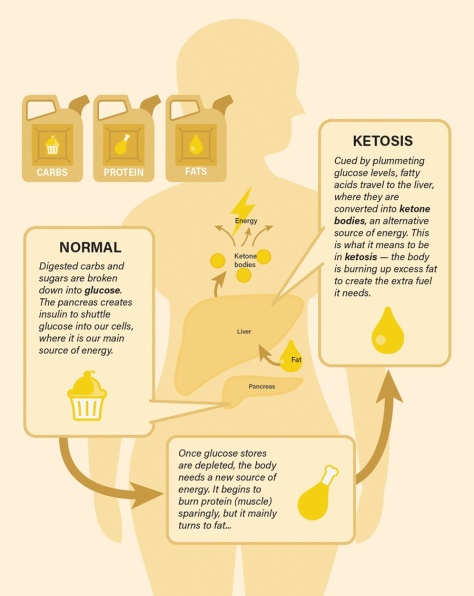
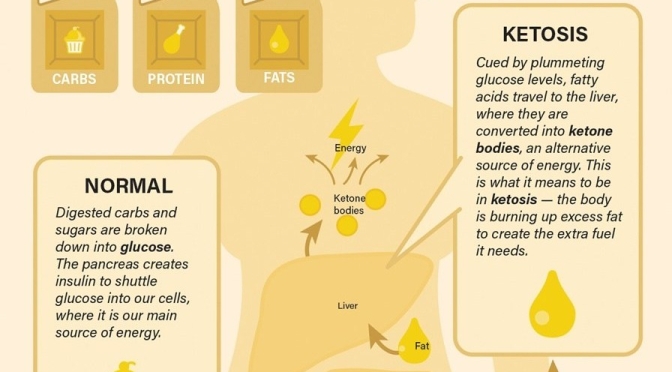
…It seems fasting triggers a dramatic switch in the body’s metabolism, according  to a paper Mattson and colleagues published in February in the experimental biology journal FASEB. In humans, fasting for 12 hours or more drops the levels of glycogen, a form of cellular glucose. Like changing to a backup gas tank, the body switches from glucose to fatty acids, a more efficient fuel. The switch generates the production of ketones, which are energy molecules that are made in the liver. “When the fats are mobilized and used to produce ketones, we think that is a key factor in accruing the health benefits,” says Mattson.
to a paper Mattson and colleagues published in February in the experimental biology journal FASEB. In humans, fasting for 12 hours or more drops the levels of glycogen, a form of cellular glucose. Like changing to a backup gas tank, the body switches from glucose to fatty acids, a more efficient fuel. The switch generates the production of ketones, which are energy molecules that are made in the liver. “When the fats are mobilized and used to produce ketones, we think that is a key factor in accruing the health benefits,” says Mattson.


 The riders who had pedaled on an empty stomach, however, had incinerated about twice as much fat during each ride as the men who consumed the shake first. The riders all had burned about the same number of calories while pedaling, but more of those calories came from fat when the men did not eat first.
The riders who had pedaled on an empty stomach, however, had incinerated about twice as much fat during each ride as the men who consumed the shake first. The riders all had burned about the same number of calories while pedaling, but more of those calories came from fat when the men did not eat first.