 Tissot consistently defied convention in both his professional and personal life. His contributions to the academy and the avant-garde are documented by participation at diverse venues such as the Paris Salon as well as London’s Royal Academy and the Grosvenor and Dudley Galleries. This exhibition explores his multifaceted career with a fresh perspective and original scholarship and will also question where and how Tissot should be situated in narratives of the nineteenth-century canon.
Tissot consistently defied convention in both his professional and personal life. His contributions to the academy and the avant-garde are documented by participation at diverse venues such as the Paris Salon as well as London’s Royal Academy and the Grosvenor and Dudley Galleries. This exhibition explores his multifaceted career with a fresh perspective and original scholarship and will also question where and how Tissot should be situated in narratives of the nineteenth-century canon.
Tissot was arguably a painter of modern life although he did not formally belong to the Impressionist circle and never exhibited in their group shows, despite an invitation from Edgar Degas.

The Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco and the Musée d’Orsay, Paris are co-organizing James Tissot: Fashion & Faith, the first major reassessment of the artist’s career in over 20 years. In San Francisco, this international retrospective will examine approximately 60 paintings, additional works on paper, and cloisonné enamels by Tissot. Exhibition highlights are drawn from the permanent collections of the Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco, including Tissot’s Self Portrait (ca. 1865) as well as prints and photographs from the Achenbach Foundation for Graphic Arts. New scholarship on the artist presented in this collaboration demonstrates that even Tissot’s most ebullient society paintings reveal rich and complex commentary on topics such as nineteenth-century society, religion, fashion, and politics, rendering him an artist worthy of reexamination in the twenty-first century.
https://legionofhonor.famsf.org/exhibitions/james-tissot-fashion-faith



 Comprising 55 Gauguin masterworks on loan from Copenhagen’s Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, as well as some 35 objects from the collection of the Saint Louis Art Museum, “Paul Gauguin: The Art of Invention,” now on view in St Louis, offers a superb overview and deep insight into the life, thought and art of this quasi-mythological being whose shadow looms large not only over artistic Modernism but over the very romantic notion of the artist who sacrifices everything for art.
Comprising 55 Gauguin masterworks on loan from Copenhagen’s Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, as well as some 35 objects from the collection of the Saint Louis Art Museum, “Paul Gauguin: The Art of Invention,” now on view in St Louis, offers a superb overview and deep insight into the life, thought and art of this quasi-mythological being whose shadow looms large not only over artistic Modernism but over the very romantic notion of the artist who sacrifices everything for art.
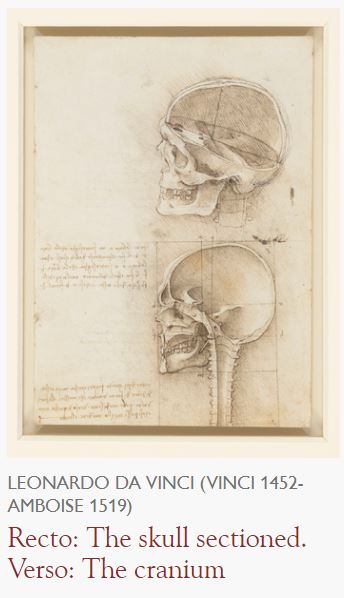 The 200 pages on display at the Queen’s Gallery, Buckingham Palace, have been together since the artist’s death. They were bound by the sculptor Pompeo Leoni in about 1590 and entered the Royal Collection during the reign of Charles II. Some of his most iconic images are here, including his study of a foetus in the womb, made as part of a treatise on anatomy that came close to being finished, but was never published.
The 200 pages on display at the Queen’s Gallery, Buckingham Palace, have been together since the artist’s death. They were bound by the sculptor Pompeo Leoni in about 1590 and entered the Royal Collection during the reign of Charles II. Some of his most iconic images are here, including his study of a foetus in the womb, made as part of a treatise on anatomy that came close to being finished, but was never published.
 In some cases, Wyeth’s images bore into memory as sharply as the books they illuminate. I’m thankful I never saw Wyeth’s “Captain Nemo” (1918) while steeping myself in Jules Verne’s “The Mysterious Island” (1874): I would never have been able to shed the image Wyeth created of this white-haired, secretive, dying man, surrounded by allusions to his exotic past, his skin seeming bleached, we learn here, by the electrical lighting of his submarine.
In some cases, Wyeth’s images bore into memory as sharply as the books they illuminate. I’m thankful I never saw Wyeth’s “Captain Nemo” (1918) while steeping myself in Jules Verne’s “The Mysterious Island” (1874): I would never have been able to shed the image Wyeth created of this white-haired, secretive, dying man, surrounded by allusions to his exotic past, his skin seeming bleached, we learn here, by the electrical lighting of his submarine.
 The Denver Art Museum will be home to the most comprehensive U.S. exhibition of Monet paintings in more than two decades. The exhibition will feature more than 120 paintings spanning Monet’s entire career and will focus on the celebrated French impressionist artist’s enduring relationship with nature and his response to the varied and distinct places in which he worked.
The Denver Art Museum will be home to the most comprehensive U.S. exhibition of Monet paintings in more than two decades. The exhibition will feature more than 120 paintings spanning Monet’s entire career and will focus on the celebrated French impressionist artist’s enduring relationship with nature and his response to the varied and distinct places in which he worked.