
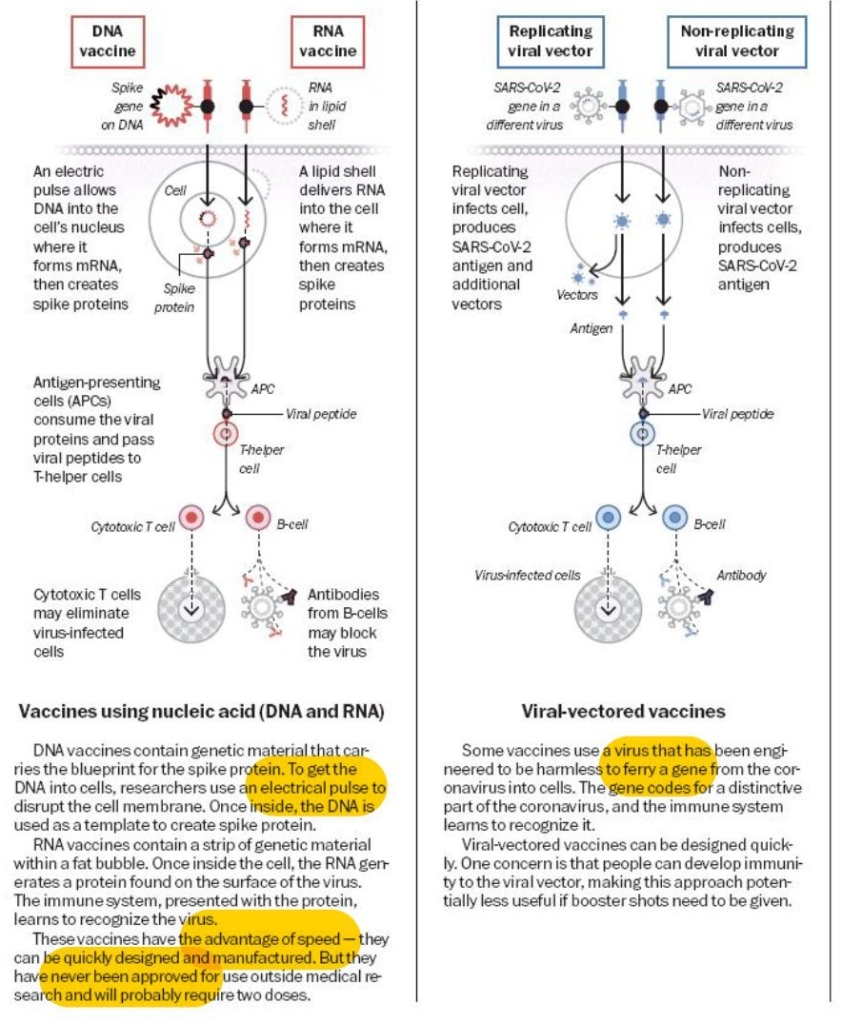
How does each of the available Covid-19 vaccines work?
Once the vaccine is injected, the mRNA is taken up by the macrophages near the injection site and instructs those cells to make the spike protein. The spike protein then appears on the surface of the macrophages, inducing an immune response that mimics the way we fight off infections and protects us from natural infection with SARS-CoV-2. Enzymes in the body then degrade and dispose of the mRNA. No live virus is involved, and no genetic material enters the nucleus of the cells.
Although these are the first mRNA vaccines to be broadly tested and used in clinical practice, scientists have been working on mRNA vaccines for years. And despite this wonderful parody piece. opens in new tab saying that the technology is “obvious,” in fact the breakthrough insight that put the mRNA inside a lipid coating to prevent it from degrading is quite brilliant — and yes, this may be the first time the New England Journal of Medicine has referenced a piece in The Onion. (Last reviewed/updated on 11 Jan 2021)
How should early side effects be managed?
Analgesics and antipyretics such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen are effective in managing post-vaccine side effects including injection-site pain, myalgias, and fever. However, the CDC does not recommend prevaccine administration of these drugs, as they could theoretically blunt vaccine-induced antibody responses.
Because of the small risk of anaphylaxis, sites that administer the vaccines must have on hand strategies to evaluate and treat these potentially life-threatening reactions. The CDC has issued recommendations on how sites should prepare. opens in new tab. (Last reviewed/updated on 11 Jan 2021)
How long will the vaccines work? Are booster doses required?
Since the vaccines have been tested only since the summer of 2020, we do not have information about the durability of protection. Data from the phase 1 trial of the Moderna vaccine suggested that neutralizing antibodies persisted for nearly 4 months. opens in new tab, with titers declining slightly over time. Given the absence of information on how long the vaccines will be protective, there is currently no specific recommendation for booster doses. (Last reviewed/updated on 11 Jan 2021)
Do the vaccines prevent transmission of the virus to others?
Many commentaries on the results of the vaccine clinical trials cite a lack of information on asymptomatic infection as a limitation in our knowledge about the vaccines’ effectiveness. Indeed, this is a theoretical concern, since up to 40% of people who get infected with SARS-CoV-2 have no symptoms but may still transmit the virus to others.
Nonetheless, there are several good reasons to be optimistic about the vaccines’ effect on disease transmission. First, in the Moderna trial. opens in new tab, participants underwent nasopharyngeal swab PCR testing at baseline and testing at week 4, when they returned for their second dose. Among those who were negative at baseline and without symptoms, 39 (0.3%) in the placebo group and 15 (0.1%) in the mRNA-1273 group had nasopharyngeal swabs that were positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR. These data suggest that even after one dose, the vaccine has a protective effect in preventing asymptomatic infection.
Second, findings from population-based studies now suggest that people without symptoms are less likely to transmit the virus to others. Third, it would be highly unlikely in biological terms for a vaccine to prevent disease and not also prevent infection. If there is an example of a vaccine in widespread clinical use that has this selective effect — prevents disease but not infection — I can’t think of one!
Until we know more, however, we should continue to emphasize to our patients that vaccination does not allow us to stop other important measures to prevent the spread of Covid-19. We need to continue social distancing, masking, avoiding crowded indoor settings, and regular hand washing. (Last reviewed/updated on 11 Jan 2021)






 “Finding a safe and effective vaccine to prevent infection with SARS-CoV-2 is an urgent public health priority,” said NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D. “This Phase 1 study, launched in record speed, is an important first step toward achieving that goal.”
“Finding a safe and effective vaccine to prevent infection with SARS-CoV-2 is an urgent public health priority,” said NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D. “This Phase 1 study, launched in record speed, is an important first step toward achieving that goal.”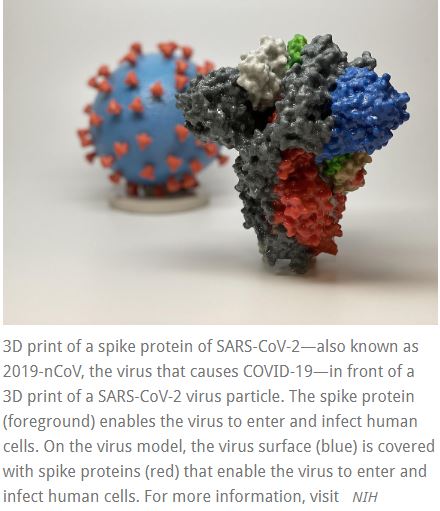 A Phase 1 clinical trial evaluating an investigational vaccine designed to protect against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has begun at Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute (KPWHRI) in Seattle. The
A Phase 1 clinical trial evaluating an investigational vaccine designed to protect against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has begun at Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute (KPWHRI) in Seattle. The